Cancer stem cells and Lon-noncRNA promotes invasion, metastasis and tumor growth in breast cancer through regulation of signaling pathway
- PMID: 40781106
- PMCID: PMC12334764
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13402-8
Cancer stem cells and Lon-noncRNA promotes invasion, metastasis and tumor growth in breast cancer through regulation of signaling pathway
Abstract
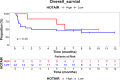
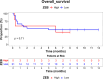
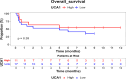
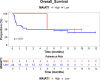
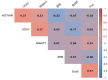
Breast cancer (BC), the most common malignant tumor in women, continues to be a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. A major challenge in managing BC, especially in metastatic cases, is the lack of reliable early diagnostic biomarkers. Metastatic breast cancer stem cells (MBCSCs) play a critical role in tumor progression, resistance to therapy, and disease recurrence. This study aimed to explore the molecular pathways connecting the long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) HOTAIR, UCA1, and MALAT1 with breast cancer stem cell-related genes FOXC2, SNAIL, and ZEB, focusing on their involvement in transcriptional regulation, proliferation, and survival. Peripheral blood samples and plasma were collected from 30 women diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer (MBC, stage IV) and 30 healthy controls. Gene expression levels were measured using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Our findings revealed a significant upregulation of SNAIL and FOXC2 in MBC patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.001). The median expression levels of SNAIL (16.4) and FOXC2 (19.5) were substantially higher in the metastatic group than in healthy individuals (SNAIL: 6.42, FOXC2: 7.23). Conversely, the expression levels of HOTAIR, UCA1, MALAT1, and ZEB did not show statistically significant differences between the two groups (p > 0.05). Correlation analysis indicated a strong positive association between FOXC2 and SNAIL expression (r = 0.41), suggesting a potential shared functional role in disease progression. These results suggest that SNAIL and FOXC2 could serve as potential prognostic biomarkers in MBCSCs, whereas HOTAIR, UCA1, MALAT1, and ZEB may not independently predict metastasis or survival outcomes. Further research is necessary to explore the therapeutic implications of these genes in metastatic breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancers; Cancer stem cell; Long non coding RNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was ethically approved by the Baheya Institutional Review Board (Baheya IRB Research Protocol Number: 202405200027).
Figures
Similar articles
-
HMGA2 associated ceRNA-HOTAIR pathway in breast cancer patients from clinicopathological perspective.Turk J Med Sci. 2025 May 30;55(3):782-791. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.6027. eCollection 2025. Turk J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40686703 Free PMC article.
-
SIAH2-AS1 stimulates breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06808-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595045 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of PVT1 inhibits cell proliferation in luminal and basal-like breast cancer subtypes by activating LATS2/Hippo signaling pathway.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul 19;23(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03944-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40684233 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin.73(1), 17–48 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Liu, S. et al. Breast cancer stem cells: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Cancer Lett.561, 216126 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

