Regional heterogeneity of the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 40781224
- PMCID: PMC12334574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61841-8
Regional heterogeneity of the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
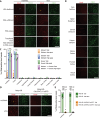
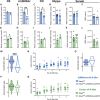
The blood-brain barrier (BBB), formed by specialized endothelial cells (ECs), regulates the extracellular composition of the central nervous system (CNS). Little is known about whether there are regional specializations of the BBB that may control the function of specific neural circuits. We use single cell RNA-seq to characterize ECs from nine CNS regions in male mice: cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, spinal cord, striatum, thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, and medulla/pons. Although there is a core BBB transcriptional profile, there are significant regional specializations. Stra6, a retinoid transporter, is highly enriched in the BBB of the nucleus accumbens shell (ShNAc) and ventral cochlear nucleus, and is controlled by dietary vitamin A, through endothelial RARƔ. EC Stra6 regulates the deposition of retinoids specifically in the ShNAc and cochlear nucleus, and is required for the function of the ShNAc, in a retinoid-dependent manner. Thus regional specializations of the BBB can regulate the function of local brain regions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zlokovic, B. V. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron57, 178–201 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Vanlandewijck, M. et al. A molecular atlas of cell types and zonation in the brain vasculature. Nature554, 475–480 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Aird, W. C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ. Res.100, 174–190 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Aird, W. C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ. Res.100, 158–173 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS103844/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS091281/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 GM111772/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS113068/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- GM008349/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 NS088353/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL086344/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1747503/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- T32 GM008349/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI036214/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- NS134680/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 NS091281/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM111772/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R21 NS113068/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS134680/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS103844/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R21 EY028647/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY028647/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HL086344/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

