Semaglutide and human reproduction: caution at the intersection of energy balance, ovarian function, and follicular development
- PMID: 40781307
- PMCID: PMC12333279
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-025-01435-7
Semaglutide and human reproduction: caution at the intersection of energy balance, ovarian function, and follicular development
Abstract
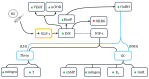
Obese or overweight patients considering IVF are generally counselled to reduce weight closer to target BMI (i.e., < 30 kg/m2) by interventions entailing dietary change with a structured exercise program. There is little disagreement that supervised weight loss can improve reproductive outcome when successful, although there are refractory cases where weight goals are unmet. Because low-grade chronic inflammation and altered immune function are characteristic of obesity and antagonize implantation, any pre-IVF weight loss facilitated by semaglutide (SG) would be helpful. However, no preclinical data have considered the ovarian implications of SG. Several formulations of SG are now available to assist in chronic weight management, treatment of type-2 diabetes, or both. SG is 31-amino acid lipopeptide with action at the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor, which augments insulin secretion while lowering hepatic glucagon output. SG thus enters a multiorgan network where insulin, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and sirtuin pathways manage ambient nutritional conditions. As GLP-1 directly influences insulin release and curtails satiety, SG adjusts many biochemical cascades where potential interference with oocyte development or embryo/endometrial crosstalk require clarification. Particularly if used outside manufacturer's guidance (i.e., for aesthetic or personal reasons), SG could bring unwelcome challenges to fertility clinics where obesity and dyslipidemia are merely exchanged for the new problems of starvation and sarcopenia. Here we examine known GLP-1 actions where energy balance, ovarian aging, and oocyte competence converge; off label SG use should be avoided until its signaling effects throughout the reproductive axis are more carefully studied.
Keywords: GLP-1; Insulin; Ovary; Reproduction; Semaglutide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indirect comparative efficacy and safety of tirzepatide 10 and 15 mg versus semaglutide 2.4 mg for the management of obesity and overweight in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Sep;27(9):4709-4719. doi: 10.1111/dom.16508. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40537987 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro maturation in subfertile women with polycystic ovarian syndrome undergoing assisted reproduction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 6;2(2):CD006606. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006606.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39912435
-
[Guidelines for the prevention and management of bronchial asthma (2024 edition)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 12;48(3):208-248. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20241013-00601. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40050074 Chinese.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for weight reduction in obesity to improve survival in women with endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):CD012513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36971688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief #360. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics 2020. doi: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db360.htm - PubMed
-
- García-Ferreyra J, Carpio J, Zambrano M, Valdivieso-Mejía P, Valdivieso-Rivera P. Overweight and obesity significantly reduce pregnancy, implantation, and live birth rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization procedures. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2021;25(3):394–402. 10.5935/1518-0557.20200105. - PMC - PubMed
-
- George JS, Srouji SS, Little SE, Ginsburg ES, Lanes A. The impact of increasing body mass index on in vitro fertilization treatment, obstetrical, and neonatal outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024;230(2):239. 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.10.018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

