Ameliorative effects of agomelatine against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 40781695
- PMCID: PMC12333101
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-025-00988-y
Ameliorative effects of agomelatine against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity
Abstract
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity is a significant impediment to the use of doxorubicin, a commonly employed chemotherapeutic agent with established efficacy in cancer treatment. The present study aimed to determine the potential protective effects of agomelatine against doxorubicin hepatotoxicity in rat toxicity models. Thirty-two rats were divided into four groups: control (with saline administration), Doxo (with 40 mg/kg doxorubicin administration), Doxo + Ago20, and Doxo + Ago40 (with 20 and 40 mg/kg agomelatine administration and 40 mg/kg doxorubicin administration). On the day of 14 rats were sacrificed, samples were collected for comparison of immunohistochemical, hematological, and biochemical analysis. There were statistically significant differences between the study groups in terms of immunohistochemical, hematological, and biochemical parameters. Agomelatine administration reduced the TNF-alpha, and caspase-3, which increased by doxorubicin, and reversed levels of oxidative stress markers altered by doxorubicin (p < 0.05). Doxorubicin induces oxidative stress, apoptosis, and hepatotoxicity. Agomelatine may be favored as a primary antidepressant to mitigate hepatic damage induced by doxorubicin.
Keywords: Agomelatine; Caspase-3; Doxorubicin; Hepatotoxicity; Oxidative stress.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
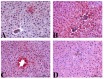
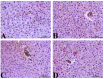
Similar articles
-
Aegeline improves doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity by modulating oxidative stress and Bax/Bcl2/caspase/NF-κB signaling.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09675-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715307 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin alleviates doxorubicin-induced hepatic damage by modulating oxidative stress: a molecular, biochemical, and histopathological approach in a rat model.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9099-9107. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03688-2. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39903256
-
Protective role of ursolic acid against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the liver of Swiss albino mice.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 12;42(8):327. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02854-7. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40652144
-
Agomelatine versus other antidepressive agents for major depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 17;2013(12):CD008851. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008851.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24343836 Free PMC article.
-
Risk prediction of hepatotoxicity in paracetamol poisoning.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017 Sep;55(8):879-892. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2017.1317349. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017. PMID: 28447858
References
-
- Alam Khan S, Jawaid Akhtar M. Structural modification and strategies for the enhanced doxorubicin drug delivery. Bioorg Chem. 2022;120:105599. - PubMed
-
- Belhadjali F, Ghrir S, Ksia F, et al. Protective effect of grape seed extract and exercise training on tissues toxicities in doxorubicin-treated healthy rat. Biomarker. 2023;28:544–54. - PubMed
-
- Prasanna PL, Renu K, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A. New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 2020;250:117599. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

