Management of pott's puffy tumor: a Delphi-method international clinical consensus statement
- PMID: 40782155
- PMCID: PMC12423165
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-025-09589-1
Management of pott's puffy tumor: a Delphi-method international clinical consensus statement
Abstract
Purpose: Pott's puffy tumor (PPT) is a rare and complex condition that requires a comprehensive diagnostic approach and multi-faceted treatment strategy. It is associated with a significant risk of intracranial complications. The purpose of this clinical consensus statement (CCS) is to systematically assess diagnostic and therapeutic approaches of patients with PPT, using the best available evidence and expertise of the panel. The results and recommendations are intended to support clinicians in making informed decisions when managing patients with PPT and to standardize diagnostic, antibiotic, and surgical management across institutions. This consensus also aimed to provide a basis for a subsequent international prospective registry to inform data-driven care.
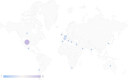
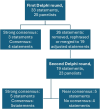
Methods: A literature review was performed via PubMed, and an international panel of 23 experts judged 33 statements in two rounds using a modified Delphi method survey to establish expert recommendations on the diagnostic considerations, medical and surgical management, and postoperative considerations. Strong consensus was defined by a mean score of ≥ 8.00 with no outliers, and consensus by a mean score of ≥ 7.00 with no more than 1 outlier.
Results: A strong consensus was reached on important aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of patients with PPT. Most pivotal are the importance of urgent imaging, imaging of the brain with a preference of MRI, the importance of broad spectrum intravenous antibiotic treatment, and the goal of surgery - resolution of the periosteal abscess and clearance of the frontal sinus drainage pathway - which can be established in various ways and is case and surgeon dependent.
Conclusion: In patients with PPT, a high index of suspicion of intracranial complications is important to prevent any delay in treatment initiation. The recommendations formulated in this international consensus statement aim to improve the diagnosis and care for patients with PPT and to address gaps and uncertainties in current guidelines. Items that did not reach consensus may serve as areas for further research.
Keywords: Acute sinusitis; Clinical guideline; Delphi consensus; Expert consensus; Intracranial abscess; Pediatric otolaryngology; Pott’s puffy tumor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to report pertaining to this study. The authors received no funding for this article or related research. Disclosures: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to report pertaining to this study. The authors received no funding for this article or related research. Ethical approval: was not required because the study did not involve any patient-related data.
Figures
References
-
- Nallani R, Wichova H, McAroy JL, Chiu AG, Villwock JA (2021) Incidence of odontogenic disease in patients with Pott’s puffy tumor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 79:389–397. 10.1016/j.joms.2020.08.001 - PubMed
-
- Klivitsky A, Erps A, Regev A, Ashkenazi-Hoffnung L, Pratt LT, Grisaru-Soen G (2023) Pott’s puffy tumor in pediatric patients: case series and literature review. Pediatr Infect Dis J 42:851–856. 10.1097/INF.0000000000004026 - PubMed
-
- Rohde RL, North LM, Murray M, Khalili S, Poetker DM (2022) Pott’s puffy tumor: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Otolaryngol 43:103529. 10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103529 - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C et al (2020) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 1–464. 10.4193/Rhin20.600 - PubMed
-
- Smiljkovic M, Tat J, Richardson SE et al (2024) A 20-year study of intracranial pyogenic complications of sinusitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 43:91–96. 10.1097/INF.0000000000004140 - PubMed