Oral cancer detection via Vanilla CNN optimized by improved artificial protozoa optimizer
- PMID: 40783415
- PMCID: PMC12335477
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11861-7
Oral cancer detection via Vanilla CNN optimized by improved artificial protozoa optimizer
Abstract
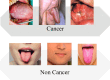
In this study, we propose a new method for oral cancer detection using a modified Vanilla Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture with incorporated batch normalization, dropout regularization, and a customized design structure for the convolutional block. An Improved Artificial Protozoa Optimizer (IAPO) metaheuristic algorithm is proposed to optimize the Vanilla CNN and the IAPO improves the original Artificial Protozoa Optimizer through a new search strategy and adaptive parameter tuning mechanism. Due to its effectiveness in search space exploration while avoiding local optimal points, the IAPO algorithm is chosen to optimize the convolutional neural network. In this study, a dataset of 1000 images of patients had published which will be preprocessed with contrast enhancement, noise reduction and data augmentation (like rotation, flipping and cropping) to generate the robust targeted model for oral cancer detection. The experimental results are evaluated against benchmark performance measures (accuracies, precision, recall, F1-score and area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC-ROC). We demonstrate through experimental results that the proposed IAPO optimized Vanilla CNN achieves a high accuracy of 92.5% which is superior than the previous state-of-the art models such as ResNet-101 (90.1%) and DenseNet-121 (89.5%). This proves to be a more trustworthy approach to oral cancer detectionbecause of the accuracy of the proposed method in comparison to denoting the supplementary results of the suggested method in contrast to other existing models.
Keywords: Cancer detection; Image classification; Improved artificial Protozoa optimizer; Metaheuristic optimization; Oral Cancer detection; Preprocessing; Vanilla convolutional neural networks.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and classification of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus images using deep spiking Q Network optimized with partial reinforcement optimizer.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Sep;196(Pt C):110863. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110863. Epub 2025 Aug 13. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40812015
-
Automatic segmentation and classification of Papanicolaou-stained cells and dataset for oral cancer detection.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Sep;180:108967. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108967. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39111154
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
References
-
- Patel, S. & Kumar, D. Predictive identification of oral cancer using AI and machine learning. Oral Oncol. Rep.13, 100697 (2025).
-
- Liu, H. & Ghadimi, N. Hybrid convolutional neural network and flexible dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm for strong kidney stone diagnosis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 91, 106024 (2024).
-
- Han, M. et al. Timely detection of skin cancer: an AI-based approach on the basis of the integration of echo state network and adapted seasons optimization algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 94, 106324 (2024).
-
- Meena, G., Mohbey, K. K. & Kumar, S. Monkeypox recognition and prediction from visuals using deep transfer learning-based neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 1–25 (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical