Multi-omics analysis of bariatric surgery's impact on type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
- PMID: 40783429
- PMCID: PMC12335437
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14577-w
Multi-omics analysis of bariatric surgery's impact on type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
Abstract
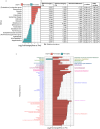
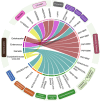
Bariatric surgery is a promising intervention for managing obesity-related metabolic disorders; however, its effects on cardiovascular disease (CVD) in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) remain poorly understood. To address this gap, we utilized a multi-omics approach to investigate how bariatric surgery influences Emirati individuals with T2D and prediabetes, focusing on the early detection of CVD markers. We longitudinally profiled 19 patients over a 9-month period, collecting omics data, including whole-genome sequencing (WGS), protein immunoassays, untargeted metabolomics, and 16S rRNA sequencing to determine gut microbiome composition. Through this study, we showed that bariatric surgery reduced CVD risk and inflammatory biomarkers while inducing changes in the gut microbiome and metabolomic profiles. We identified four inflammatory biomarkers (FGF-basic, TNFSF13, IL-8, and IL-1Ra) that were significantly altered following surgery (p < 0.05). Additionally, we identified 98 metabolites that showed significant changes after surgery that are involved in folate biosynthesis, glycerophospholipid, and retinol metabolism. Eighteen microbial genera were found to differentiate between the pre- and post-surgery states. Our analysis revealed four microbial genera (Enterobacter, Enterococcus, Gemella, and Erysipelotrichaceae UCG-003) associated with two T2D SNPs (rs11830243 and rs6978118) and three CVD SNPs (rs9490306, 62207434, and rs34606058). These genera formed the network's central hub, connecting host genetic variants, metabolic pathways, and clinical data, highlighting their role in host-microbiome interactions. The study quantifies the impact of phenotypic factors on CVD progression among UAE nationals, contributing to a deeper understanding of cardiometabolic health within this population.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Cardiovascular disease; Omics; Precision medicine; Prognosis; Risk predictor; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis reveals the functional signature of microbes and metabolomics in pre-diabetes individuals.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0145924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01459-24. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40488467 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of prediabetes and diabetes on endothelial function in a large population-based cohort.Blood Press. 2024 Dec;33(1):2298309. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2023.2298309. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Blood Press. 2024. PMID: 38185988
-
Multi-omics integration reveals functional signatures of gut microbiome in atherosclerosis.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2542384. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2542384. Epub 2025 Aug 10. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 40785047 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of bariatric surgery on gut microbiota in obese patients: A systematic review.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug;44(4):457-477. doi: 10.1007/s12664-025-01763-x. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40220249
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for people with cardiovascular disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 25;10(10):CD013650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013650.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus. (Wiley, 2015). 10.1002/9781118387658.
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas Eighth Edition. http://dx.doi. org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8. (2017).
-
- Home et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021 | IDF Diabetes Atlas. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/ (2021).
-
- Alkharaiji, M., Anyanwagu, U., Donnelly, R. & Idris, I. Effect of bariatric surgery on cardiovascular events and metabolic outcomes in obese patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Obes. Surg.29, 3154–3164 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Aakre, K. M. et al. Gastric bypass surgery is associated with reduced subclinical myocardial injury and greater activation of the cardiac natriuretic peptide system than lifestyle intervention. Clin. Biochem.86, 36–44 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

