Periodontitis-associated Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes ulcerative colitis by ferroptosis-mediated gut barrier disruption
- PMID: 40783488
- PMCID: PMC12335446
- DOI: 10.1038/s41522-025-00763-1
Periodontitis-associated Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes ulcerative colitis by ferroptosis-mediated gut barrier disruption
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Periodontitis-associated Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes ulcerative colitis by ferroptosis-mediated gut barrier disruption.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025 Oct 1;11(1):191. doi: 10.1038/s41522-025-00821-8. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025. PMID: 41034277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
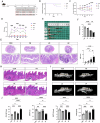
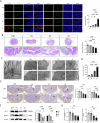
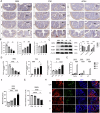
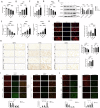
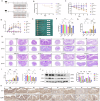
Periodontitis and ulcerative colitis (UC) are inflammatory diseases linked through the "gum-gut" axis. Fusobacterium nucleatum, an important periodontitis-associated pathobiont and gastrointestinal opportunist, may mediate their comorbidity. This study investigated the role of F. nucleatum in UC using dextran sulfate sodium-induced UC and F. nucleatum-induced periodontitis models. F. nucleatum exacerbated inflammatory alveolar bone loss and intestinal barrier dysfunction, accelerating UC severity. Integrated 16S rRNA gene sequence and LC-MS metabolomics revealed ferroptosis activation, characterized by elevated Fe2+ and malondialdehyde, glutathione depletion, dysregulated GPX4, FTH1, and ACSL4 expression, reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, and reactive oxygen species aggregation in the mouse colon and colonic epithelial cell CCD841. Administration of ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1 attenuated UC by restoring intestinal permeability, preserving mucin layers, and enhancing tight junction proteins ZO-1 and CLDN-1. These findings establish F. nucleatum as a key mediator of periodontitis-UC comorbidity through ferroptosis-mediated gut barrier disruption, providing mechanistic insights into microbial-driven inflammatory cross-talk.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 82301089/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC0553/Develop Program, the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RCDWJS2024-(2)/West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- RD-03-202105/Research and Develop Program, West China Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

