Generalized linear modeling of flow cytometry data to analyze immune responses in tuberculosis vaccine research
- PMID: 40783500
- PMCID: PMC12335546
- DOI: 10.1038/s41540-025-00572-4
Generalized linear modeling of flow cytometry data to analyze immune responses in tuberculosis vaccine research
Abstract
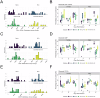
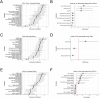
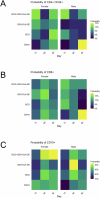
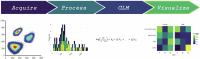
Tuberculosis (TB) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) kills ~1.3 million people annually. Accordingly, vaccines and sophisticated analytical tools are necessary to evaluate their effectiveness. To address these challenges, we created a Generalized Linear Model (GLM) framework to evaluate high-dimensional flow cytometry data and the multivariable influences on immune responses, accommodating proportional and non-normal data, and violations of assumptions set by classical statistical evaluations. In naïve mice vaccinated with BCG boosted with ID93-GLA-SE, we used GLMs to assess the impact of sex, vaccination, and days post-infection on probabilities of immune cell phenotypes following Mtb challenge. We demonstrate enhanced T cell responses in the lung following BCG + ID93-GLA-SE compared to BCG or ID93-GLA-SE alone, with notable sex differences in humoral immunity. This framework highlights GLMs in assessing complex datasets while enhancing our comprehension of independent continuous and categorical variables on vaccine efficacy, and serves as a foundation for deeper, more complex scenarios.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Geneva: World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. (ed World Health Organization). https://iris.who.int/ (World Health Organization, 2023).
-
- Fatima, S., Kumari, A., Das, G. & Dwivedi, V. P. Tuberculosis vaccine: a journey from BCG to present. Life Sci.252, 117594 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

