Effect of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40783544
- PMCID: PMC12335772
- DOI: 10.1186/s13102-025-01270-8
Effect of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
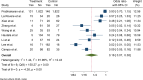
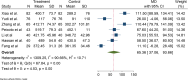
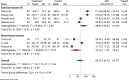
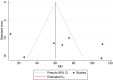
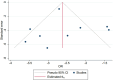
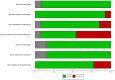
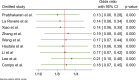
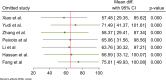
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) poses a significant threat to cardiovascular health. This study evaluates the effects of structured exercise cardiac rehabilitation (CR) both center-based and home-based on incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and 6 min Walk Test (6MWT) in ACS patients.A systematic literature search was conducted across major databases to identify randomized controlled trials (RCT) published from 2000 to March 2024. Random-effects model was applied for meta-analysis. Cochran's Q and I2 values were applied to determine heterogeneity, followed by subgroup analyses for exploring sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity and publication bias analyses were performed.Ten RCTs showed that rehabilitation significantly reduced the odds of MACE compared to usual care (OR: 0.16, 95% CI: 0.07-0.38; p = 0.00). In terms of type of rehabilitation, center-based CR had a lower odd of MACE (OR: 0.13) than home-based CR (OR: 0.37), though the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.24). In terms of follow-up duration, studies with ≤ 1 year follow-up reported lower MACE odds (OR: 0.10) compared to those > 1 year (OR: 0.28), also not statistically significant (p = 0.33). For functional capacity, analysis of seven studies showed that rehabilitation significantly improved 6MWT performance. Exercise-based rehabilitation led to an average increase of 86.24 m, Home-based rehabilitation showed a smaller gain of 37.63 m, with a significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.04).This meta-analysis provides strong evidence that CR, particularly structured exercise-based programs, significantly reduces the risk of MACE and improves functional capacity in patients with cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Exercise; Myocardial infarction; Rehabilitation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sadeghi M, Shabib G, Masoumi G, Amerizadeh A, Shahabi J, Heidari R, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the prevalence of smoking cessation in cardiovascular patients after participating in cardiac rehabilitation. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;46(3):100719. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

