Successful management of a delayed-presented and complicated right ventricular pseudoaneurysm: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 40783555
- PMCID: PMC12335073
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-025-03566-9
Successful management of a delayed-presented and complicated right ventricular pseudoaneurysm: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Right ventricle (RV) pseudoaneurysm is a substantially rare but fatal condition that should be diagnosed promptly to prevent severe complications, such as rupture and death. However, due to its nonspecific presentation, its diagnosis relies mainly on advanced imaging cardiac modalities. This report describes the successful management of a delayed and unusual presentation of RV pseudoaneurysm.
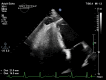
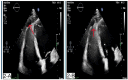
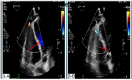
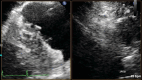
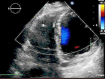
Case presentation: A 31-year-old white male patient with a history of pericardiectomy presented with chest pain and dyspnea, which worsened by exertion, and edema of the lower extremities, which had started several weeks ago and had been exacerbated over time. The initial evaluations with cardiac enzyme check, chest X-ray, and electrocardiogram were unremarkable, and the patient was planned to undergo a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE). TTE revealed RV failure and increased RV diameter; a suspicious lesion in the RV apex was also detected, suggesting a pseudoaneurysm. Cardiac Computed Tomography (CTA) confirmed the diagnosis, and interventional treatment via an Amplatzer device was considered, which was rejected by the interventional cardiologist of the center due to the lack of experience and logistics for such intervention. Considering the patient's condition deterioration, the patient was transferred to an operating room, and an open-heart surgery was performed to suture the ruptured RV myocardium. The pericardial effusion was removed. The histopathological evaluation of the sample confirmed the diagnosis. The post-surgical recovery and follow-up were uneventful. The graphical abstract is added below to illustrate the case and summarize it.
Conclusion (clinical key point): Right ventricle pseudoaneurysms can present with unusual symptoms and signs, and misdiagnosis is highly probable. Advanced imaging techniques after the initial echocardiogram might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Moreover, timely, appropriate, and wisely chosen treatment (interventional or surgical) can result in uneventful treatment and recovery.
Keywords: Cardiac imaging; Cardiac surgery; Case report; Echocardiography; Pseudoaneurysm; Right ventricle.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: The patient provided written informed consent to participate in this clinical case report, ensuring that all personal information and medical data will be kept confidential and used solely for research purposes. Consent for publication: The patient provided informed consent for the publication of this report, and the center’s ethical policy performed the procedure. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Yeo TC. Clinical profile and outcome in 52 patients with cardiac pseudoaneurysm. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(4):299. - PubMed
-
- Baccouche H, Ursulescu A, Yilmaz A, Ott G, Klingel K, Zehender M, et al. Right ventricular false aneurysm after unrecognized myocardial infarction 28 years previously. Circulation. 2008;118(20):2111–4. - PubMed
-
- Calabrò R, Santoro G, Pisacane C, Pacileo G, Russo MG, Vosa C. Repeat syncopal attacks due to postsurgical right ventricular pseudoaneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68(1):252–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

