A novel method for assessing postmortem interval using radon radioisotopic decay - an internal radon 'time of death clock'
- PMID: 40783585
- PMCID: PMC12335445
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15168-5
A novel method for assessing postmortem interval using radon radioisotopic decay - an internal radon 'time of death clock'
Abstract
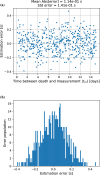
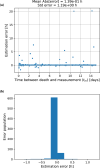
Estimating the postmortem interval (PMI)-the time since death-remains a longstanding challenge in forensic and biological sciences due to the complex influence of environmental and physiological variables. Here, we present a novel computational framework that leverages the physical principles of radioactive decay to estimate PMI using the relative isotope abundances of radon progeny ([Formula: see text], [Formula: see text], and [Formula: see text]) in biological tissue. Our approach models the decay chain of inhaled [Formula: see text] and solves the associated system of differential equations to determine PMI based on isotope ratio dynamics. A key innovation is the use of paired measurements taken at two postmortem time points to capture the time-derivative of the decay curve, enhancing solution uniqueness, reducing dependence on prior exposure history, therefore minimizing error. Monte Carlo simulations were employed to assess model performance. If validated empirically, this approach lays the groundwork for a physics-based method for PMI estimation with potential applications in forensic science and radiation biology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ruiz López, J. L. & Partido Navadijo, M. Estimation of the post-mortem interval: a review. Forensic science international369, 112412 (2025). - PubMed
-
- Madea, B. Handbook of Forensic Medicine (John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated, Newark, 2014), 1 edn.
-
- Sutton, L. & Byrd, J. An introduction to postmortem interval estimation in medicolegal death investigations. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2, e1373, 10.1002/wfs2.1373 (2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RGPIN-2020-04212/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- RGPIN-2023-05167/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- RGPIN-2023-05167/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- 39871/Canada Foundation for Innovation
- 39871/Canada Foundation for Innovation
- No number available/Alberta Cancer Foundation
- No number available/Alberta Cancer Foundation
- No number available/Arnie Charbonneau Cancer Institute, University of Calgary
- No number available/Arnie Charbonneau Cancer Institute, University of Calgary
- No number available/Ministry of Economic Development and Trade, Government of Alberta
- No number available/Ministry of Economic Development and Trade, Government of Alberta
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

