Synthesis of piperazine-based benzimidazole derivatives as potent urease inhibitors and molecular docking studies
- PMID: 40783587
- PMCID: PMC12335596
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14723-4
Synthesis of piperazine-based benzimidazole derivatives as potent urease inhibitors and molecular docking studies
Abstract
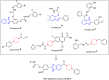
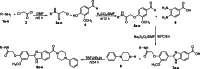
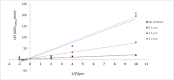
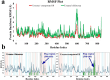
The development of new bioactive compounds is important for progress in therapeutic research. In the present study, we describe the multistep synthetic approach to develop a library of novel benzimidazole analogs incorporating piperazine rings in order to increase their biological activity. In order to synthesize the desired benzimidazole analogs, the synthesis started with the easily accessible precursors between aniline and chloroacetyl chloride. It proceeded via a series of reactions, such as condensation, cyclization, and N-alkylation. TLC optimized each step, and spectroscopic methods such as CHN, IR, EIMS, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR were used to characterize the final products. The urease inhibitory activity of the synthesized compounds was evaluated. It was discovered that almost all compounds were quite effective, even more potent (IC50 = 0.15-12.17 µM) than the standard thiourea (IC50 = 23.11 ± 0.21 µM). The structure-activity relationship (SAR) is also established, which displayed that compound 9 L (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.09 µM) with -NO2 substitutions at meta position play a major role in urease inhibition and figure out as the most potent analog of the library. These results were further verified by molecular docking analysis, which indicated favorable binding energies and interactions of the compounds with the urease active site. This study not only depicts the importance of multistep synthesis but also the structure-based modification approach to produce new pharmacophores for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Benzimidazole; Docking study; Piperazine; Urease inhibition.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Benzimidazole-acrylonitrile hybrid derivatives act as potent urease inhibitors with possible fungicidal activity.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(20):2151-2168. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2393570. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39297549
-
Synthesis, in vitro anti-urease, in-silico molecular docking study and ADMET predictions of piperidine and piperazine Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adducts (MBHAs).Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2024 Nov 20;80(7-8):361-373. doi: 10.1515/znc-2024-0175. Print 2025 Jul 28. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39565962
-
Novel benzimidazole-based azine derivatives as potent urease inhibitors: synthesis, in vitro and in silico approach.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(22):2337-2350. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2401311. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39311079
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keri, R. S., Hiremathad, A., Budagumpi, S. & Nagaraja, B. M. Comprehensive review in current developments of benzimidazole-based medicinal chemistry. Chem. Biology Drug Des.86 (1), 19–65 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Taha, M. et al. Synthesis of benzimidazole derivatives and their antiglycation, antioxidant, antiurease and molecular Docking study. Arab. J. Chem.17 (4), 105700 (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

