A dilemma study of the traffic flow system emerged due to the lane-change by follower's tailgating effect
- PMID: 40783591
- PMCID: PMC12335528
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14760-z
A dilemma study of the traffic flow system emerged due to the lane-change by follower's tailgating effect
Abstract
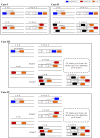
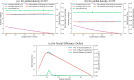
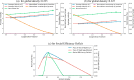
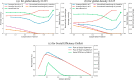
In this study, an artificial traffic system, which is generated on a computer by utilizing the computational technique, has been developed by establishing brilliant lane-changing criteria for the Cellular Automata (CA) traffic model to figure out adequate strategies for cooperative driving that can be implemented in actual traffic systems for optimum use of existing road facilities. We investigate the flow efficiency and social dilemma, which embody the tension between the demanded road facility and the existing road facility, that emerged due to the defector drivers in a traffic flow system, who are highly aggressive in driving and impose threatening/pushing effects on their preceding while they are tailgating. The evolutionary game theory, which is one of the most efficient tools in the decision-making process, has been utilized to identify the Social Efficiency Deficit (SED), which means the dilemma strength of those games. We introduced a new lane-changing protocol for the preceding vehicle, considering the threatening effects given by the aggressive follower. This investigation explored several case studies defining various strategies for cofactors and defectors. We conducted a series of multi-agent simulations on this traffic flow system and experienced the Prisoner's Dilemma (PD) and the Quasi-Prisoner's Dilemma game with diverse dilemma strengths for four different strategies for cooperators and defectors.
Keywords: Evolutionary game; Follower’s tailgating effect; Intelligent traffic system; Social dilemma in traffic system.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Vision screening of older drivers for preventing road traffic injuries and fatalities.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 21;2014(2):CD006252. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006252.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24563119 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Thunig, T., Kühnel, N. & Nagel, K. Adaptive traffic signal control for real-world scenarios in agent-based transport simulations. Transp. Res. Procedia. 37, 481–488. 10.1016/j.trpro.2018.12.215 (2019).
-
- Nance, O. et al. Alescio-Zonta: Improved understanding and control of traffic flow has become a fast-growing area of scientific research mathematical theory of automobile traffic. Protides BioI. Fluids, Proc. Colloq. 180, 1195 (1957).
-
- Kerner, B. S., Klenov, S. L. & Wolf, D. E. Cellular automata approach to three-phase traffic theory. J. Phys. Math. Gen.35, 9971. 10.1088/0305-4470/35/47/303 (2002).
-
- Kearney, M. J. Exactly solvable cellular automaton traffic jam model. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys.74, 061115. 10.1103/PHYSREVE.74.061115/FIGURES/2/MEDIUM (2006). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

