The relationship between postoperative proximal junctional kyphosis and MRI-based pedicle bone quality scores in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
- PMID: 40783762
- PMCID: PMC12335139
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-025-03104-3
The relationship between postoperative proximal junctional kyphosis and MRI-based pedicle bone quality scores in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Abstract
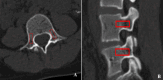
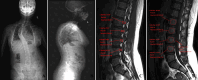
Objective: Proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) is a major postoperative complication in patients with thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), and poorer bone quality condition is an important risk factor for the occurrence of PJK, meanwhile osteopenia in patients with AIS can persist into adulthood. The use of computed tomography Hounsfield units (CT-HU) and Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) to assess the quality of the pedicle bone condition can predict the occurrence of postoperative Proximal junctional problems (PJP). However, there is a lack of an MRI-based site-specific bone quality scoring system for assessing the condition of pedicle bone quality and its relationship with PJK. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to create an MRI-based site-specific bone quality scoring system for the pedicle and to evaluate its correlation with pedicle CT-HU values and its ability to predict thoracic AIS PJK, comparing the predictive ability of the Pedicle Bone Quality (PBQ) Score and the Vertebral Bone Quality (VBQ) Score.
Methods: This is a retrospective study to assess the relationship between postoperative PJK and the PBQ and VBQ scores in patients with Lenke1 and 2 AIS. Demographics, procedure-related data, and radiological data were collected, PBQ and VBQ values were measured on MRI T1-weighted unenhanced sagittal images, respectively. Simple linear regression and Pearson correlation analyses were used to determine the relationship of PBQ and VBQ score with pedicle HU values and Proximal junctional angle (PJA). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify risk factors associated with PJK, and in addition, univariate linear regression analyses were used to identify potential factors associated with PBQ score. Finally, Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and area-under-the-curve values were used to assess the predictive ability of PBQ and VBQ scores.
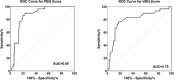
Results: A total of 181 patients (mean age 15.44 ± 3.22 years) were included in this study and the PJK occurred in 30 (16.6%) patients. and patients in the PJK group had significantly higher PBQ and VBQ values (3.25 ± 0.34; 3.69 ± 0.27) than those in the non-PJK group (2.65 ± 0.51; 2.86 ± 0.53; P < 0.001). Simple linear regression analyses showed a significant negative correlation between PBQ and VBQ with the pedicle HU values (r=-0.639, P < 0.001; r=-0.592, P < 0.001), and a significant positive correlation was found between PBQ (r = 0.642; P < 0.001), VBQ (r = 0.608; P < 0.001) with PJA. The results of multivariate logistic regression showed that the PBQ score was the risk factor for PJK (OR = 3.763, 95% CI = 4.324-12.844, P < 0.001), with 86.3% predictive accuracy, higher than VBQ (79.2%).
Conclusions: The novel PBQ score is a reliable tool for predicting postoperative PJK in patients with thoracic AIS. Compared to the VBQ score, it has a better correlation with pedicle CT-HU values and PJA, as well as better predictive ability for PJK.
Keywords: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; MRI; Pedicle bone quality score; Proximal junctional kyphosis; Site-specific bone quality score; Vertebral bone quality score.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This retrospective study was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The ethics committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University approved this study. Because this is a retrospective study, it was approved by the Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University to waive informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable, our manuscripts do not contain any identifiable individual images or information. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The utility of MRI-based S1 vertebral bone quality score in assessing bone mineral density for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6426-6435. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-2209. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727348 Free PMC article.
-
Vertebral bone quality score as a novel predictor of proximal junctional kyphosis after thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery.Eur Spine J. 2023 Nov;32(11):3996-4002. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-07894-z. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Eur Spine J. 2023. PMID: 37606725
-
Tri-cortical pedicle screw fixation in the most cranial instrumented segment to prevent proximal junctional kyphosis.Spine J. 2025 Aug;25(8):1698-1707. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2025.02.002. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Spine J. 2025. PMID: 39993503
-
Proximal junctional kyphosis in pediatric spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review and critical analysis.Spine Deform. 2022 Mar;10(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s43390-021-00429-w. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Spine Deform. 2022. PMID: 34704232
-
Intraoperative image guidance compared with free-hand methods in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis posterior spinal surgery: a systematic review on screw-related complications and breach rates.Spine J. 2017 Sep;17(9):1215-1229. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Spine J. 2017. PMID: 28428081
References
-
- Kim HJ, Lenke LG, Shaffrey CI, Van Alstyne EM, Skelly AC. Proximal junctional kyphosis as a distinct form of adjacent segment pathology after spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(22 Suppl):S144–164. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Iyer S. Proximal junctional kyphosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(5):318–26. - PubMed
-
- Hart R, McCarthy I, Oʼbrien M, Bess S, Line B, Adjei OB, Burton D, Gupta M, Ames C, Deviren V, et al. Identification of decision criteria for revision surgery among patients with proximal junctional failure after surgical treatment of spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(19):E1223–1227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2024YFFK0248/the Key R&D projects of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
- JH2024047/Tibet Regional Science and Technology Programme Key R&D and Transformation Projects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

