Severe Staphylococcus aureus infection: associated factors and outcomes
- PMID: 40784249
- PMCID: PMC12357306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2025.104573
Severe Staphylococcus aureus infection: associated factors and outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: Staphylococcus aureus causes potentially life-threatening infections, with a somber prognosis when the infection is caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus due to limited treatment options. The present study describes serious infections by S. aureus in patients hospitalized in an infectious disease's unit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between 2016 and 2021.
Material and methods: This was a retrospective study based on data from positive samples diagnosed by the microbiology laboratory and by review of medical records. Clinical-demographic variables and outcomes were compared between Patients Living with HIV (PLHIV) and non-HIV patients. Data were analyzed using Jamovi 1.6 and R 4.0.1 statistical software.
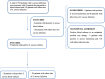
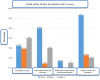
Results: A total of 67 patients with a serious S. aureus infection were identified, of whom 29 presented bacteremia and 38 other infections. Thirty-one of 67 (46.3%) were PLHIV. The median age of all patients was 46years, although PLHIV were significantly younger than non-HIV individuals (36 vs. 60 years-old, p < 0.001). The median CD4 lymphocyte count was 95 cells/mm3. Community infection occurred in 36/67 (53.7%) patients, of whom 19/36 (52.7%) had bacteremia. A total of 20 MRSA infections (29.9% of the patients) were identified, which accounted for 14/36 (38.8%) of the community infections. More than a third of PLHIV (38.7%) had MRSA, and all these were sensitive to cotrimoxazole. No difference in mortality was found between PLHIV and non-HIV patients, nor between the MRSA and MSSA groups. Bacteremia was present in 29 patients; MRSA accounted for 9 (31.0%) of these. The 30-day mortality was 4/9 (44.4%) and 2/20 (10%) in MRSA and MSSA bacteremia, respectively.
Conclusions: The most frequent comorbidity in patients with severe S. aureus infections was HIV, with a high rate of MRSA infections recorded in PLHIV. PLHIV were younger, but did not suffer higher mortality, although they did have more relapses and new staphylococcal infections.
Keywords: Bacteremia; HIV/AIDS; MRSA; Mortality; Staphylococcus aureus.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roberts S., Chambers S. Diagnosis and management of Staphylococcus aureus infections of the skin and soft tissue. Intern Med J. 2005;35(Suppl 2):S97–105. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas R., Carricajo A., Morel J., Rigaill J., Grattard F., Guezzou S., et al. Evaluation of effectiveness and compliance with the mupirocin nasal ointment part of Staphylococcus aureus decolonization in real life using UPLC-MS/MS mupirocin quantification. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75:1623–1630. - PubMed
-
- Hidron A.I., Kourbatova E.V., Halvosa J.S., Terrell B.J., McDougal L.K., Tenover F.C., et al. Risk factors for colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in patients admitted to an urban hospital: emergence of community-associated MRSA nasal carriage. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:159–166. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

