Relationship between thromboembolic events and thrombopoietin receptor agonists: a pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System and the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report
- PMID: 40784768
- PMCID: PMC12336560
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-099153
Relationship between thromboembolic events and thrombopoietin receptor agonists: a pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System and the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report
Abstract
Objective: Thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs) are widely used in thrombocytopenia, yet their association with thromboembolic events (TEEs) remains concerning. This study aimed to assess the real-world TEE risk associated with TPO-RAs.
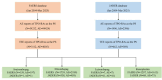
Design: Retrospective pharmacovigilance analysis of the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) and Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) databases.
Setting: Both FAERS and JADER were searched from January 2004 to March 2025.
Main outcome measures: Disproportionality analyses were performed using reporting OR (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), informational component (IC) and empirical Bayesian geometric mean (EBGM) to identify potential safety signals.
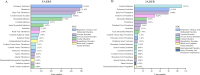
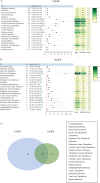
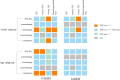
Results: 4005 TEE from FAERS and 569 from JADER were analysed. Venous TEE showed higher prevalence and signal intensity (FAERS: n=1489, ROR 4.19, PRR 4.14, EBGM05 3.94, IC025 0.37; JADER: n=269, ROR 15.95, PRR 14.27, EBGM05 12.56, IC025 2.14). Lusutrombopag had the strongest TEE signal (FAERS: n=7, ROR 8.80, PRR 7.77, EBGM05 4.00, IC025 1.25; JADER: n=41, ROR 38.02, PRR 16.94, EBGM05 11.45, IC025 2.38). FAERS identified 49 positive signals, while JADER identified 30, with 20 signals overlapping. Subgroup analysis indicated males had higher arterial TEE risk with TPO-RAs, while females had higher venous TEE risk in both FAERS and JADER. In FAERS, elderly (≥60 years) showed elevated arterial TEE risk with TPO-RAs and romiplostim, while non-elderly had higher venous TEE risk with avatrombopag and eltrombopag.
Conclusions: The study provided real-world evidence of TEE associated with TPO-RAs, highlighting a strong link despite variations in signal values and regional reporting practices. Findings underscore ongoing clinical safety surveillance for TPO-RAs.
Keywords: Adverse events; CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY; Thromboembolism.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety evaluation of irinotecan: a real-world disproportionality analysis using FAERS and JADER databases during the time period 2004-2024.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 9;16:1516449. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1516449. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40552159 Free PMC article.
-
Safety analysis of romiplostim, eltrombopag, and avatrombopag post-market approval: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Feb 27;26(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00873-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40016824 Free PMC article.
-
Post-marketing safety profile of ganirelix in women: a 20-year pharmacovigilance analysis of global adverse drug event databases (2004-2024).BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Apr 22;26(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00920-4. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40264185 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombopoietin mimetics for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 30;9(9):CD009883. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009883.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28962071 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombopoietin receptor agonists for prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumours.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 27;11(11):CD012035. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012035.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29178132 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
