M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles protect against abdominal aortic aneurysm by modulating macrophage polarization through miR221-5p
- PMID: 40784924
- PMCID: PMC12335759
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-025-00768-w
M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles protect against abdominal aortic aneurysm by modulating macrophage polarization through miR221-5p
Abstract
Background: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from M2 macrophages (M2-EVs) play a protective role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. However, their roles and mechanisms in abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) are unknown.
Methods: The effects of M2-EVs in AAA were examined in ApoE-/- mice with angiotensin II infusion. After M2 macrophages were stimulated with antisense oligonucleotides of miR221-5p (miR221-5p-ASOs), EVs were extracted and administered to mice via the tail vein. In vitro, the primary bone marrow-derived monocytes (BMDMs) were isolated and co-cultured with human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) in Transwell chambers.
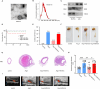
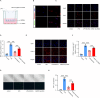
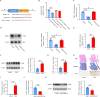
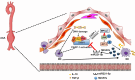
Results: M2-EVs significantly reduced AAA incidence and maximal aortic diameters, improved fiber continuity, increased α-SMA, and reduced macrophage infiltration in AAA mice. RNA sequencing revealed that miR221-5p was upregulated in M2-EVs and downregulated in AAA. miR221-5p-ASOs reduced the protection of M2-EVs in AAA mice. M2-EVs induced M2 macrophage polarization, while miR221-5p-ASOs had no effect. Moreover, M2-EVs alleviated oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in HAECs. Mechanistically, miR221-5p bound to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) mRNA and reduced PARP-1 expression; PARP-1 was bound to protein phosphatase 1ɑ (PP-1ɑ) and negatively regulated its expression. In vitro experiments showed miR221-5p modulated macrophage polarization through the PARP-1/PP-1ɑ/JNK/c-Jun pathway. Macrophage deletion of PARP-1 inhibited AAA formation and phosphorylation of JNK/c-Jun in mice.
Conclusions: miR221-5p in M2-EVs plays a critical role in AAA pathophysiology by modulating macrophage polarization through PARP-1/PP-1ɑ/JNK/c-Jun signaling. M2-EVs and miR221-5p represent promising therapeutic options for AAA.
Keywords: Abdominal aortic aneurysm; Extracellular vesicles; M2 macrophages; Macrophage polarization; microRNA 221-5p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Helsinki Declaration and Basel Declaration. All procedures were conducted following protocols approved by the Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University (KYLL-202107-104 and DWLL-2019-117) and adhered to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH). The patients or relatives provided their written informed consent for patient participation in this study. Consent for publication: All authors approved the final manuscript to be published. Competing interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Golledge J. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: update on pathogenesis and medical treatments. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(4):225–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

