Analysis of the value of infrared thermal imaging technology in the diagnosis of emergency pulmonary infections
- PMID: 40784954
- PMCID: PMC12336340
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15123-4
Analysis of the value of infrared thermal imaging technology in the diagnosis of emergency pulmonary infections
Abstract
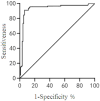
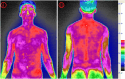
To explore the value of infrared thermal imaging technology in the diagnosis of emergency pulmonary infections. 200 patients who received emergency treatment at our hospital from October 2020 to December 2021 were selected as the study subjects. General information was collected from all patients, including 108 patients with acute pulmonary infection and 92 patients without pulmonary infection. All patients were tested using infrared thermal imaging technology and infrared thermal imaging equipment, with X-ray examination as the gold standard, The chest X-ray scan was performed using an X-ray camera produced by Siemens, and the temperature difference between the affected areas detected by infrared thermal imaging technology in two groups of patients was compared. The detection rate of infrared thermal imaging in the lung infection group was analyzed, and the diagnostic efficacy was evaluated by plotting the ROC curve to calculate the area under the curve. Compared with the uninfected group, the infrared radiation temperature of the infected group was significantly increased in the body surface, chest, abdomen, bilateral lungs, and midpoint of the breasts, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The positive rate of infrared thermal imaging detection in the lung infection group was 93 cases (86.11%), and the positive rate of gold standard X-ray detection was 102 cases (94.44%), the difference is statistically significant (P < 0.05). The AUC value of infrared thermal imaging technology for detecting emergency pulmonary infection patients is 0.933, the sensitivity is 90.36%, the specificity is 92.28%, and the Jordan index is 0.92. Infrared thermography has important applications in the diagnosis of lung infections in emergency medicine.It can reflect the distribution range of abnormal hot spots in patients' lung infections by evaluating temperature changes, and has good diagnostic value in clinical practice.
Keywords: Diagnostic value; Emergency pulmonary infection; Infrared thermal imaging technology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng, L. et al. Co-infection of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and pulmonary CMV in a infant with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Diagn. Cytopathol.49 (9), E340–E343 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, X. et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae infection associated septic pulmonary embolism in an emergency department from East China. Ann. Palliat. Med.10 (2), 1521–1529 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- A2018305/Accurate localization, qualitative and quantitative study of infrared thermal imaging in patients with acute upper respiratory tract infection
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
- 202010570004/Expression analysis and clinical grading of cobra bite wound by infrared thermal imaging (National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project for College Students)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources