Integrative systems biology and in-vitro analysis of cryptolepine's therapeutic role in breast cancer
- PMID: 40784974
- PMCID: PMC12336106
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03158-y
Integrative systems biology and in-vitro analysis of cryptolepine's therapeutic role in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most diagnosed cancer in women and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Chemotherapy faces challenges like drug resistance, side effects, and recurrence, underscoring the need for innovative therapies. This study explores cryptolepine, a natural compound, for its therapeutic potential against heterogeneous BC by targeting specific molecular mechanisms.
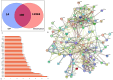
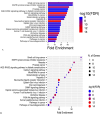
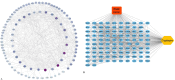
Methods: we conducted an ADMET analysis to assess cryptolepine's pharmacokinetic properties and drug-likeness. Target prediction was performed using SWISS-TARGET-PREDICTION and Integrative Pharmacology for BC. Identified targets were cross-referenced with BC-related genes from Gene Atlas, TCGA, and OMIM. Protein-protein interactions were analyzed using STRING, and pathway enrichment was assessed using KEGG and ShinyGO. Molecular docking and dynamics simulations evaluated cryptolepine's binding efficacy while in-vitro assays, including proliferation studies and mRNA expression analysis, validated these findings.
Results: Cryptolepine demonstrated favorable drug-likeness and multi-target activity, interacting with key cancer pathways such as p53, STAT3, and PI3K-Akt. Network pharmacology revealed its potential to reduce drug resistance. Cryptolepine regulated important genes (PTGS2, STAT3, CCND1) across critical pathways (cAMP, PI3K/AKT, P53, IL6/JAK2/STAT3). Molecular docking confirmed strong binding (ΔG - 8.2 kcal/mol), and in-vitro assays showed IC50 values of 4.6 μM for MDA-MB-231 and 3.1 μM for Mcf-7. mRNA expression analysis indicated increased cytochrome C and BAX, while pro-caspase levels decreased.
Conclusion: Cryptolepine shows promise as a therapeutic candidate for BC. Future research should optimize its pharmacological profile for specificity and reduced toxicity.
Keywords: BC; Cryptolepine; P53; STAT3; Signaling pathways.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucidating the Mechanism of Xiaoqinglong Decoction in Chronic Urticaria Treatment: An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.2174/0115734099391401250701045509. Online ahead of print. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40676786
-
Understanding mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum-derived exosome-like nanoparticles against breast cancer through an integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology analysis.Front Chem. 2025 Jun 6;13:1559758. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1559758. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40547857 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of phytoconstituents from selected Egyptian plants against non-small cell lung cancer using integrated in vitro network pharmacology and molecular docking approach.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9061-9082. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03834-4. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39888361 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abacha YZ, Forkuo AD, Gbedema SY, Mittal N, Ottilie S, Rocamora F, Winzeler EA, van Schalkwyk DA, Kelly JM, Taylor MC, Reader J, Birkholtz LM, Lisgarten DR, Cockcroft JK, Lisgarten JN, Palmer RA, Talbert RC, Shnyder SD, Wright CW. Semi-synthetic analogues of cryptolepine as a potential source of sustainable drugs for the treatment of malaria, human African trypanosomiasis, and cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 875647. 10.3389/fphar.2022.875647. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrijauskaite K, Wargovich MJ. Role of natural products in breast cancer related symptomology: targeting chronic inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;80:370–8. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.08.011. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–9. 10.1038/75556. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atale N, Gupta S, Yadav UCS, Rani V. Cell-death assessment by fluorescent and nonfluorescent cytosolic and nuclear staining techniques. J Microsc. 2014;255(1):7–19. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
