Tianma Granules Alleviate AOM/DSS-Induced Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation
- PMID: 40785041
- PMCID: PMC12336053
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70772
Tianma Granules Alleviate AOM/DSS-Induced Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation
Abstract
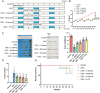
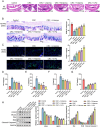
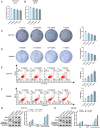
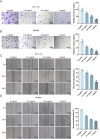
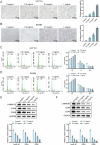
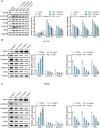
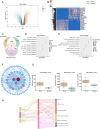
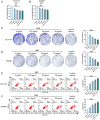
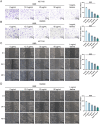
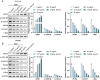
This study aimed to investigate the anti-tumour effect and the possible molecular mechanism of Tianma granules on colorectal cancer (CRC). The therapeutic effect of Tianma granules on CRC cell lines (HT116 and SW480) and AOM/DSS-induced CRC mouse models was evaluated. Tianma granules can attenuate weight loss and increase the survival rate of CRC mice, restore reduced colon length, reduce tumour numbers and increase goblet cell numbers in CRC mice. Tianma granules also downregulated the level of CRC-specific markers (COX2 and MUC2), inhibited the inflammation (decreased TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 levels and increased INF-γ level), and promoted apoptosis (decreased TUNEL positive cell rate; decreased Bax and Cleaved caspase3 protein levels and increased Bcl2 level) in CRC mice. In vitro, Tianma granules can inhibit the viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells, while promoting cell apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and cell senescence. Tianma granules promoted AXIN1 protein levels and inhibited p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, Wnt5a and Cyclin D1 and c-Myc protein levels. Moreover, the network pharmacology analysis and in vitro validation revealed berberine might be the key compound responsible for Tianma granules' pharmacological actions. In conclusion, Tianma granules can inhibit inflammation and tumour progression in AOM/DSS-induced CRC mice, as well as inhibit CRC cell malignant phenotype. The protection of Tianma granules against CRC may be achieved by inhibiting the Wnt signalling pathway.
Keywords: AOM/DSS; Tianma granules; Wnt signalling pathway; colorectal cancer; inflammation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3-O-Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic Acid Suppresses Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting the NF-Kb Signaling Pathway and Remodeling Gut Microbiota.Oncol Res. 2025 Jul 18;33(8):1969-1989. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.062386. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40746878 Free PMC article.
-
A novel drug prejudice scaffold-imidazopyridine-conjugate can promote cell death in a colorectal cancer model by binding to β-catenin and suppressing the Wnt signaling pathway.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:615-632. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.022. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39067696 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol inhibits invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(7):3587-3598. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04265-x. Epub 2022 Aug 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35960375 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between tumor cells and immune cells of the colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment: Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1587950. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587950. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Mesenchymal Markers in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 4;52(1):673. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10745-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613936 Review.
References
-
- Sandhu J., Lavingia V., and Fakih M., “Systemic Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in the Era of Precision Medicine,” Journal of Surgical Oncology 119, no. 5 (2019): 564–582. - PubMed
-
- Sethy C. and Kundu C. N., “5‐Fluorouracil (5‐FU) Resistance and the New Strategy to Enhance the Sensitivity Against Cancer: Implication of DNA Repair Inhibition,” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 137 (2021): 111285. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

