YTK Display-and-Secrete: Screening for Optimal Protein Secretion Elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 40785119
- PMCID: PMC12455636
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00264
YTK Display-and-Secrete: Screening for Optimal Protein Secretion Elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
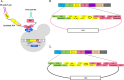
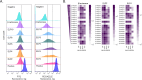
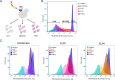
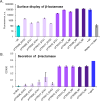
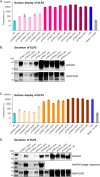
Engineering yeast to secrete target proteins requires searching for optimal combinations of promoters and signal peptides so that genes can be composed that give a high expression and efficient secretion. Most methods for this involve laborious, one-by-one assessments or require the use of enzymatic reporter proteins in order to achieve high-throughput capacity. Here, we introduce a novel modular method for the high throughput screening of yeast strains designed to secrete proteins of interest. Our approach integrates combinatorial DNA assembly, yeast surface display, flow cytometry, and nanopore DNA sequencing to facilitate rapid screening. Building on a widely used yeast toolkit (YTK) for modular cloning, our system creates surface display libraries with N- and C-terminal epitope tags by fast DNA assembly and genome-integration into Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Flow cytometry with fluorescently labeled epitope-binding antibodies identifies strains that secrete and display the most full-length protein and can rapidly sort these from low secretors. We demonstrate our system by optimizing the secretion of the enzyme beta-lactamase and several elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs), first identifying strains with modular genetic element combinations that give the best surface display and then validating that removal of the surface-display anchor protein in these strains gives a high target protein secretion. We then show how pooled long read sequencing of sorted cells can determine the effectiveness of numerous combinations of promoters and signal peptides for a target protein in a single experiment. The data sets from this offer new insights into an optimal element choice for efficient protein secretion and could train machine learning models.
Keywords: nanopore sequencing; protein secretion; yeast surface display; yeast toolkit.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

