Cognitive Impairment in CMV Seropositive and CMV Seronegative Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 40785852
- PMCID: PMC12333801
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001818
Cognitive Impairment in CMV Seropositive and CMV Seronegative Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Background: Kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) experience a high burden of cytomegalovirus infection (CMV R+) and long-term premature cognitive aging. We tested whether CMV was associated with post-KT cognitive impairment.
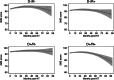
Methods: In a 2-center prospective cohort study of 574 KTRs (mean age: 54.7 y), we obtained CMV donor/recipient (D/R) serostatus and measured pre- and post-KT cognitive function using the Modified Mini-Mental State Examination. We estimated post-KT global cognitive function trajectories by CMV serostatus using adjusted mixed effect models with linear spline terms.
Results: Two hundred twenty-two (38.6%) recipients were CMV D+/R+, 100 (17.4%) were CMV D+/R-, 153 (26.6%) were CMV D-/R+, and 99 (17.2%) were CMV D-/R-. At the time of KT, there were no significant differences in global cognitive function scores among KTRs irrespective of CMV D/R status. Cognitive function equally improved in all CMV D/R groups during the first 3 y post-KT (slope = 0.62 points/year; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.17-1.07). However, during years 3-8 post-KT, the global cognitive function score trajectories significantly declined in the CMV D+/R+ KTRs (slope = -3.51 points/year; 95% CI, -5.07 to -1.95) but not in the other groups, including CMV D-/R- (slope = 0.44 points/year; 95% CI, -2.12 to 3.00; P = 0.01), CMV D-/R+ (slope = 0.13 points/year; 95% CI, -1.83 to 2.09), or CMV D+/R- (slope = 0.01 points/year; 95% CI, -1.87 to 1.89).
Conclusions: CMV D+/R+ KTRs may be at elevated risk for post-KT cognitive impairment; clinicians may prioritize early interventions in this population.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex and gender as predictors for allograft and patient-relevant outcomes after kidney transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 19;12(12):CD014966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014966.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39698949
-
Belatacept for kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 24;2014(11):CD010699. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010699.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25416857 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral medications for preventing cytomegalovirus disease in solid organ transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 3;5(5):CD003774. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003774.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38700045 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-emptive treatment for cytomegalovirus viraemia to prevent cytomegalovirus disease in solid organ transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jan 14;1(1):CD005133. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005133.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39807668
-
Interleukin 2 receptor antagonists for kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;2010(1):CD003897. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003897.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20091551 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

