Prognostic significance of cold pressor test myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with ischemia and nonobstructive coronary arteries
- PMID: 40785860
- PMCID: PMC12332663
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2025-33
Prognostic significance of cold pressor test myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with ischemia and nonobstructive coronary arteries
Abstract
Correspondence to: Cunzhi Lu, MD. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Xuzhou Central Hospital, No. 199, Jiefangnan Road, Xuzhou 221009, China. Email: 13912045900@163.com; Yuetao Wang, MD. Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, No. 185, Juqian Street, Changzhou 213003, China; Institute of Clinical Translation of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Soochow University, Changzhou, China. Email: yuetao-w@163.com.
Background: Ischemia with nonobstructive coronary arteries (INOCA) is prevalent among patients with angina, is linked to major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), and is often driven by endothelial dysfunction. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of the cold pressor test (CPT) in identifying individuals at elevated risk for MACEs among patients with INOCA.
Methods: A total of 124 INOCA inpatients were included in the retrospective cohort study. Clinical data including age, gender, BMI, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus (DM), active smoking, and symptoms were collected from medical records. A positive CPT-myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) result was considered to be the presence of a reversible perfusion defect with a summed difference score (SDS) ≥2. The patients were routinely followed-up according to standard protocol. An MACE was defined as a composite endpoint including all-cause mortality, late coronary revascularization [≥3 months following single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-MPI], nonfatal myocardial infarction, rehospitalization due to angina, heart failure, and stroke.
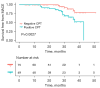
Results: The number of positive CPT-MPI cases was 49 (39.5%) and that of negative CPT-MPI cases was 75 (60.5%). Compared with negative CPT-MPI, positive CPT-MPI group had a higher percentage of DM [16 (32.7%) vs. 13 (17.3%)], coronary atherosclerosis [33 (67.3%) vs. 32 (42.7%)], and ST-T segment changes on routine admission electrocardiogram (ECG) [37 (75.5%) vs. 42 (56.0%)] (all P values <0.05). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses indicated coronary atherosclerosis as independent risk factor for positive CPT-MPI [odds ratio (OR) 2.68, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.22-5.90; P=0.014]. The proportion of positive CPT-MPI was higher in patients with MACEs than in patients without them [6 (32.7%) vs. 16 (8%); P <0.05]. In the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model, only positive CPT-MPI (hazard ratio 2.97, 95% CI: 1.02-8.58; P=0.04) was significantly associated with MACE occurrence.
Conclusions: Among patients with INOCA <39.5% had positive CPT, which was significantly related to MACE occurrence. In patients with positive CPT, the risk of MACE increased twofold. Coronary atherosclerosis was the independent risk factor of positive CPT. CPT-MPI offers valuable insights for risk stratification and treatment decision-making in patients with INOCA, particularly in identifying those at higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Cold pressor test (CPT); endothelium dysfunction; ischemia and nonobstructive coronary arteries (INOCA); myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2025-33/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Smoking cessation for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 8;8(8):CD014936. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014936.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35938889 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction.Health Technol Assess. 2004 Jul;8(30):iii-iv, 1-207. doi: 10.3310/hta8300. Health Technol Assess. 2004. PMID: 15248938
-
Beta-blockers in patients without heart failure after myocardial infarction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 5;11(11):CD012565. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012565.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34739733 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radico F, Zimarino M, Fulgenzi F, Ricci F, Di Nicola M, Jespersen L, Chang SM, Humphries KH, Marzilli M, De Caterina R. Determinants of long-term clinical outcomes in patients with angina but without obstructive coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 2018;39:2135-46. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy185 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feenstra RGT, Boerhout CKM, Woudstra J, Vink CEM, Wittekoek ME, de Waard GA, Appelman Y, Eringa EC, Marques KMJ, de Winter RJ, Beijk MAM, van de Hoef TP, Piek JJ. Presence of Coronary Endothelial Dysfunction, Coronary Vasospasm, and Adenosine-Mediated Vasodilatory Disorders in Patients With Ischemia and Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2022;15:e012017. 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.122.012017 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
