Peritumoral and intratumoral magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics of brain metastases for predicting the response to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40785874
- PMCID: PMC12332723
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2024-2671
Peritumoral and intratumoral magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics of brain metastases for predicting the response to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The early prediction of treatment response for EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) is critical to guiding therapy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study aimed to develop a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based radiomics model based on intratumoral and peritumoral regions to assess the response of patients with metastatic NSCLC to EGFR-TKIs.
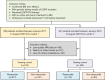
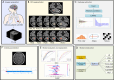
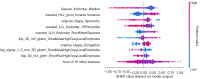
Methods: We retrospectively recruited 418 and 160 patients with brain metastases (BMs) from EGFR-mutant NSCLC who received EGFR-TKI therapy from hospital 1 and hospital 2, respectively. The intratumoral region of interest (ROI_I) was manually segmented for contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (T1-CE) imaging. Five peritumoral ROIs (ROI_P) at 2-, 4-, 6-, 8-, and 10-mm expansions along ROI_I were defined, and combined ROIs (ROI_I and ROI_P) were automatically generated. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used to select the most predictive features, which was followed by the construction of radiomics models (the ROI_I model, ROI_P model, and the combined model). The area under the curve (AUC) and Shapley method were used to validate the performance of the models and explain the best models.
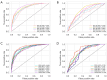
Results: The combined intratumoral and peritumoral 6-mm regions achieved the best performance, with AUCs of 0.913 and 0.826 in the training and test cohort. The ROI_I model also demonstrated a degree of classification power in both the training and test cohort, with AUCs of 0.868 and 0.762, respectively.
Conclusions: As compared to models consisting of intratumoral or peritumoral radiomics features alone, the model combining intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics features achieved better performance in predicting therapeutic response to EGFR-TKIs. The optimal combined region model with 6-mm peritumoral expansion along the tumor may benefit the clinical treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR; Radiomics; brain metastases (BMs); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); peritumoral.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2024-2671/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Tang M, Xu M, Wang J, Liu Y, Liang K, Jin Y, Duan W, Xia S, Li G, Chu H, Liu W, Wang Q. Brain Metastasis from EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Secretion of IL11 from Astrocytes Up-Regulates PDL1 and Promotes Immune Escape. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2024;11:e2306348. 10.1002/advs.202306348 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosen J, Werner JM, Ceccon GS, Rosen EK, Wollring MM, Stetter I, Lohmann P, Mottaghy FM, Fink GR, Langen KJ, Galldiks N. MRI and (18)F-FET PET for Multimodal Treatment Monitoring in Patients with Brain Metastases: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. J Nucl Med 2024;65:838-44. 10.2967/jnumed.123.266687 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
