Comparison of six surrogate insulin resistance indices for predicting the accumulation of pericardial fat on noncontrast computed tomography
- PMID: 40785897
- PMCID: PMC12332731
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2025-250
Comparison of six surrogate insulin resistance indices for predicting the accumulation of pericardial fat on noncontrast computed tomography
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance is closely associated with pericardial fat. In this prospective study, we aimed to compare the utility of six surrogate insulin resistance indices, including the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, TyG-waist circumference (TyG-WC), TyG-waist-to-height ratio (TyG-WHtR), lipid accumulation production (LAP), visceral adiposity index (VAI), and Chinese VAI (CVAI) in predicting pericardial fat accumulation on noncontrast computed tomography.
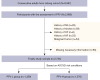
Methods: The six surrogate insulin resistance indices (TyG, TyG-WC, TyG-WHtR, LAP, VAI, and CVAI) were calculated using their respective formulae. The pericardial fat volume (PFV) was obtained from noncontrast computed tomography scans and categorized into PFV-low (PFV-L) and PFV-high (PFV-H) via the Youden statistic according to the risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). A logistic regression model, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and generalized additive model were used for statistical analyses.
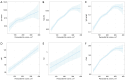
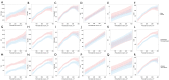
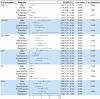
Results: Overall, 2,735 adults were analyzed. The TyG, TyG-WC, TyG-WHtR, LAP, VAI, and CVAI were significantly higher in the PFV-H group than in the PFV-L group. All six insulin resistance surrogates showed significant positive correlations with PFV. The CVAI demonstrated the highest predictive value for assessing PFV, followed by TyG-WC, TyG-WHtR, LAP, TyG, and VAI. The CVAI was associated with the largest increase in PFV based on the original model [age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)] as compared to the other insulin resistance indices.
Conclusions: The TyG, TyG-WC, TyG-WHtR, LAP, VAI, and CVAI were positively associated with PFV in patients without overt cardiovascular diseases. The CVAI may effectively reflect PFV accumulation.
Keywords: Chinese visceral adiposity index (CAVI); Pericardial fat; insulin resistance.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2025-250/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between various insulin resistance surrogates and gallstone disease based on national health and nutrition examination survey.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09482-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670519 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Novel Triglyceride- and Triglyceride-Glucose-Derived Obesity Indices with Hypertension in Nonobese US Adults (NHANES 1999--2020).Am J Hypertens. 2025 Aug 1:hpaf146. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaf146. Online ahead of print. Am J Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 40747643
-
The Predictive Value of Insulin Resistance Surrogates for Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Aug;16(8):1649-1663. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01765-0. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40517339 Free PMC article.
-
Does diabetes status modify the association between the triglyceride-glucose index and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 4;24(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02890-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40760488 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-specific accuracy of lipid accumulation product index for the screening of metabolic syndrome in general adults: a meta-analysis and comparative analysis with other adiposity indicators.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jun 26;23(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02190-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38926783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding J, Hsu FC, Harris TB, Liu Y, Kritchevsky SB, Szklo M, Ouyang P, Espeland MA, Lohman KK, Criqui MH, Allison M, Bluemke DA, Carr JJ. The association of pericardial fat with incident coronary heart disease: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am J Clin Nutr 2009;90:499-504. 10.3945/ajcn.2008.27358 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zamani SK, Sarma S, MacNamara JP, Hynan LS, Haykowsky MJ, Hearon CM, Wakeham D, Brazile T, Levine BD, Zaha VG, Nelson MD. Excess Pericardial Fat Is Related to Adverse Cardio-Mechanical Interaction in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2023;148:1410-2. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065909 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
