Preoperative computed tomography-guided localization for pulmonary nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis of soft hook-wire and coil localization
- PMID: 40785912
- PMCID: PMC12332689
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2025-56
Preoperative computed tomography-guided localization for pulmonary nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis of soft hook-wire and coil localization
Abstract
Background: Preoperative computed tomography (CT)-guided analysis of pulmonary nodule (PN) localization is performed to increase the success of resection surgery using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). This meta-analysis compared the relative efficacy and safety of soft hook-wire (SHW) and coil-based strategies for CT-guided PN localization.
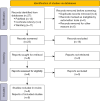
Methods: The databases of PubMed, Wanfang, and Cochrane Library were searched to acquire relevant studies published before September 2024 using the following search query: (((coil) AND ((((localization needle) OR (anchored needle)) OR (Sens-cure needle)) OR (soft hook-wire))) AND (localization)) AND ((lung nodule) OR (pulmonary nodule)). The acquired related outcomes were pooled and analyzed.
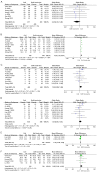
Results: This meta-analysis included 8 studies, including 440 patients undergoing CT-guided coil localization for 502 PNs and 446 patients undergoing CT-guided SHW localization for 521 PNs. The results indicated that the SHW and coil groups had similar pooled localization success rates (P=0.13), pulmonary hemorrhage rates (P=0.28), limited resection duration (P=0.91), pneumothorax rates (P=0.18), and entire VATS duration (P=0.07). Furthermore, SHW localization analysis was substantially faster than coil localization analysis (P=0.0009). Moreover, there was significant heterogeneity in the endpoints of localization duration (I2=95%) and limited resection duration (I2=76%). In addition, there was no publication bias in any endpoints.
Conclusions: This study indicated that both coil- and SHW-based CT-guided PN localization can inform limited resection using VATS with similar safety and success rates. However, compared to coil localization, SHW localization is time saving.
Keywords: Coil; computed tomography (CT); localization; pulmonary nodule (PN); soft hook-wire (SHW).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2025-56/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of computed tomography-guided hook-wire localization technique in thoracoscopic surgery for small pulmonary nodules (≤ 10 mm).J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023 Apr 5;18(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02188-3. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37020219 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative computed tomography guided coil versus suture hook-wire localization for multiple pulmonary nodules.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jun 6;23(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03871-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40481541 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative computed tomography-guided soft hook-wire localization for multiple pulmonary nodules.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 21;15:1501165. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1501165. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40061898 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Preoperative Lung Localization for Pulmonary Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):316-328. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Chest. 2017. PMID: 27717643
-
Localization techniques for guided surgical excision of non-palpable breast lesions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 31;2015(12):CD009206. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009206.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26718728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L, Shen S, Qu T, Feng T, Huang X, Chi R, Hu F, Xiao H. Feasibility and safety of computed tomography-guided intrapulmonary injection of indocyanine green for localization of peripheral pulmonary ground-glass nodules. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2023;13:7052-64. 10.21037/qims-23-117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
