Research Progress on Nucleus-Targeting Carbon Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging and Therapy
- PMID: 40785951
- PMCID: PMC12335257
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S520205
Research Progress on Nucleus-Targeting Carbon Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging and Therapy
Abstract
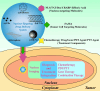
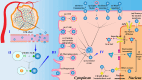
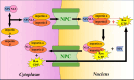
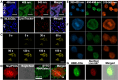
The cell nucleus, as the central hub of cellular physiological activities, represents an effective target for cancer therapy. Targeting strategies aimed at the cell nucleus can enhance the delivery of more drugs into the tumor cell nucleus, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy. Such approaches can overcome the limitations of previous tissue- and cell-level treatments, such as insufficient specificity and excessive toxic side effects. Currently, researchers have integrated carbon nanoparticles (CNPs), therapeutic molecules, and nucleus-targeting components to construct various nucleus-targeted carbon nanoparticle delivery systems for tumor imaging and treatment. These systems not only increase drug concentration within the cell nucleus but also enable certain CNPs to utilize their intrinsic fluorescence for imaging monitoring. This review summarizes the latest classification progress of nucleus-targeted CNPs, their mechanisms of action in cancer-targeted diagnosis and treatment, and their applications in cancer therapy. Additionally, the article discusses the current challenges and future directions in this field, aiming to provide valuable reference information for precision cancer treatment.
Keywords: carbon nanoparticles; nucleus-targeting; tumor imaging and therapy.
© 2025 Mu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Exploring the Potentials of Hyaluronic Acid-coated Polymeric Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Treatment by Precision Drug Delivery, Tackling Drug Resistance, and Reshaping the Tumour Micro Environment.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(20):3960-3999. doi: 10.2174/0109298673302510240328050115. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38571347 Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Structural modification strategies for ferritin nanoparticles and their applications in biomedicine: a narrative review.Nanoscale. 2025 Jul 31;17(30):17428-17442. doi: 10.1039/d5nr01369k. Nanoscale. 2025. PMID: 40668604 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of co-delivery nanoparticle drug delivery systems in non-small cell lung cancer: A review.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Oct;254:114795. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114795. Epub 2025 May 19. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 40403441 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

