From traditional remedy to modern therapy: a comprehensive review of palmatine's multi-target mechanisms and ethnopharmacological potential
- PMID: 40786032
- PMCID: PMC12331620
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1624353
From traditional remedy to modern therapy: a comprehensive review of palmatine's multi-target mechanisms and ethnopharmacological potential
Abstract
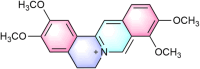
Background: As a core active metabolite of traditional Chinese medicines including Coptis chinensis Franch. and Phellodendron amurense Rupr., palmatine has been employed in Asian traditional medicine for centuries, primarily for treating jaundice, liver diseases, and inflammatory disorders. Modern research reveals that this isoquinoline alkaloid exhibits multi-target regulatory properties, demonstrating broad therapeutic potential across various diseases. This review systematically elucidates the molecular mechanisms of palmatine in treating digestive system disorders, neurological diseases, metabolic diseases, cancer and so on and cancers, with particular emphasis on analyzing its "disease-target-pathway" relationships.
Methods: In accordance with the PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase databases. The search terms included "Palmatine," "Disease," "in vitro/in vivo experiment," "Inflammation," "Anti-inflammatory," and "Antioxidation." among others. The search covered all English-language articles related to palmatine published between 1 January 2014, and 31 May 2025. All included studies underwent a quality assessment.
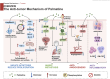
Results: Studies demonstrate palmatine's multi-target mechanisms through regulation of NF-κB/NLRP3, Nrf2/HO-1, and AMPK/mTOR signaling pathways, mediating anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and metabolic-modulating effects. Its exceptional blood-brain barrier permeability confers distinct advantages for central nervous system disorders, while its metabolites such as 8-oxypalmatine display superior bioactivity. In anticancer applications, palmatine functions through multiple mechanisms encompassing direct tumor cell cytotoxicity, metastasis suppression, and angiogenesis inhibition, while maintaining dose-dependent safety characteristics.
Conclusion: Palmatine serves as a bridge connecting traditional medicine and modern therapy, offering novel strategies for complex diseases through its polypharmacological actions. Although limited by low bioavailability, clinical potential can be enhanced via combination therapies, structural modifications such as C13 alkylation, and nano-delivery systems. Future research should prioritize exploration of synergistic effects, targeted delivery technologies, and large-scale clinical validation.
Keywords: metabolism; molecular mechanism; multiple target point; palmatine; pharmacology; traditional botanical drug medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Han, Yang, Lu, Shi and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Multiple target and regulatory pathways of berberine.Phytomedicine. 2025 Oct;146:157030. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157030. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40763599 Review.
-
Deciphering the therapeutic potential of Sinigrin: A promising anti-inflammatory agent for chronic disease management.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156875. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156875. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40505485 Review.
-
Rabdosia rubescens (Hemsl.) H. Hara: A potent anti-tumor herbal remedy - Botany, phytochemistry, and clinical applications and insights.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;340:119200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119200. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39631716
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

