What are the best clinical management strategies for cardiomyopathy? an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- PMID: 40786045
- PMCID: PMC12331498
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1544121
What are the best clinical management strategies for cardiomyopathy? an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to summarize and evaluate the quality of evidence regarding the effectiveness and safety of different interventions for patients with cardiomyopathy, based on published meta-analyses through an umbrella review.
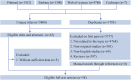
Materials and methods: The literature was searched via PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library. Two reviewers evaluated the methodological quality of the included articles using the AMSTAR score. In addition, according to the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE), evidence of each outcome was evaluated and graded as "high," "moderate," "low," or "very low" quality for drawing conclusions. Additionally, each outcome was classified into four categories (classes I-IV and nonsignificant).
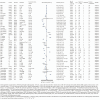
Results: High-quality evidence suggested that for patients with cardiomyopathy, stem cell treatment could significantly improve left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular ejection volume, 6-min walk distance (6-MWD), and New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification. High-quality evidence also suggested that for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), adding traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) such as Qili Qiangxin capsule (QQC), Shenmai injection (SMI), Zhigancao, and Shengmai to conventional Western medical treatment could significantly improve clinical effects, including LVEF, 6-MWD, and reductions in inflammatory indicators, left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD), left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), and heart rate. In addition, high-quality evidence suggested that for patients with DCM, drugs such as atorvastatin, carvedilol, thyroid hormone, and L-carnitine could significantly improve LVEF and cardiac output and reduce C-reactive protein levels, systolic blood pressure, LVEDD, and left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes. Furthermore, implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) therapy could significantly reduce sudden cardiac death.
Conclusion: High-quality evidence showed that cell therapy, atorvastatin, carvedilol, and thyroid hormone have significant improvement effects on the prognosis of cardiomyopathy. In addition, combining traditional Chinese medicines with conventional Western medicine therapy could significantly improve the effectiveness of conventional Western medicine therapy for cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; intervention; prognosis; treatment; umbrella review.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Wang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelazeem B., Abbas K. S., Ahmad S., Raslan H., Labieb F., Savarapu P. (2022). The effect of angiotensin II receptor blockers in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 23 (4), 141. 10.31083/j.rcm2304141 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

