Machine learning based insights into cardiomyopathy and heart failure research: a bibliometric analysis from 2005 to 2024
- PMID: 40786090
- PMCID: PMC12331722
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1602077
Machine learning based insights into cardiomyopathy and heart failure research: a bibliometric analysis from 2005 to 2024
Abstract
Background: Cardiomyopathy and heart failure are among the most critical challenges in modern cardiology, with increasing attention to the integration of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) for diagnostics, risk prediction, and therapeutic strategies. This study was aimed at evaluating global research trends, influential contributions, and emerging themes in the domain of cardiomyopathy and heart failure from 2005 to 2024.
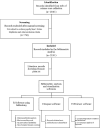
Methodology: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database. The study utilized the R- package bibliometrix-biblioshiny, VOSviewer, Scimago Graphica and CiteSpace to analyze the publications on cardiomyopathy, heart failure, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Key metrics examined included top institutions, countries, journals, keywords, co-authorship networks, and keyword co-occurrence patterns. Additionally, the analysis evaluated publication counts, citation trends, H-index, and collaboration metrics to identify research trends and emerging themes in the field.
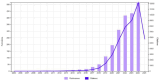
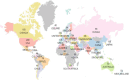
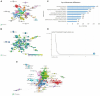
Results: A total of 2,110 publications retrieved from the last 20 years were included in the analysis. The United States of America (USA), China, and the United Kingdom (UK), emerged as leading contributors, with institutions such as Mayo Clinic and Harvard University producing high-impact research. Dominant keywords included "heart failure," "risk," "diagnosis," and "artificial intelligence," reflecting the increasing reliance on ML for predictive analytics. Thematic evolution revealed a transition from traditional classification methods to advanced techniques, including feature selection and proteomics. Influential studies, including those by Friedman PA, Noseworthy PA, and Attia ZI, showcased the transformative potential of AI in cardiology. Global collaboration networks underscored strong partnerships but highlighted disparities in contributions from low-income regions.
Conclusion: This analysis highlights the dynamic evolution of cardiomyopathy research, emphasizing the critical role of ML and AI in advancing diagnostics and therapeutic strategies. Future research should address challenges in scalability, data standardization, and ethical considerations to ensure equitable access and implementation of these technologies, particularly in underrepresented regions.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; artificial intelligence; bibliometric; cardiomyopathy; heart failure; machine learning.
Copyright © 2025 Akram, Nawaz, Yuxing, Zhang, Haixin, Liu, Qian and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

