Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis After Face and Neck Rhytidectomy: A Case of Locus Minoris Resistentiae
- PMID: 40786140
- PMCID: PMC12333704
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000007052
Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis After Face and Neck Rhytidectomy: A Case of Locus Minoris Resistentiae
Abstract
We report a case of a 52-year-old woman who developed acute localized exanthematous pustulosis, a rare drug reaction, after cefazolin administration for a face and neck surgery. The rash was confined to the surgical areas, suggesting a locus minoris resistentiae, a phenomenon where a site of previous injury becomes more vulnerable to a subsequent insult. The rash resolved with corticosteroids. We review the clinical features, causes, and management of acute localized exanthematous pustulosis.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Seminario-Vidal is an employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Billington is a consultant for Becton Dickinson. The other authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures

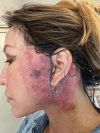

References
-
- Safa I, Ines L, Noureddine L, et al. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis: clinical features, pathophysiology, and therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e15087. - PubMed
-
- Opstrup MS, Johansen JD, Zachariae C, et al. Contact allergy to chlorhexidine in a tertiary dermatology clinic in Denmark. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;74:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Guerra KC, Toncar A, Krishnamurthy K. Miliaria. StatPearls Publishing; September 2024. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537176/. Accessed July 28, 2025. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
