NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix (PolyNovo) for Aesthetic Nasal Reconstruction: A Case Report of Rhinophyma Resurfacing
- PMID: 40786324
- PMCID: PMC12335319
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87678
NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix (PolyNovo) for Aesthetic Nasal Reconstruction: A Case Report of Rhinophyma Resurfacing
Abstract
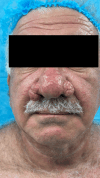
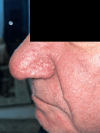
Rhinophyma, a severe form of rosacea, causes significant nasal disfigurement, posing challenges for aesthetic reconstruction after excision. This case report details the novel application of PolyNovo's NovoSorb® biodegradable temporizing matrix (BTM), a synthetic dermal substitute, for aesthetic nasal reconstruction following rhinophyma excision and utilizing secondary intention healing. A 65-year-old male with progressive rhinophyma underwent tangential excision and burring. A tailored piece of NovoSorb® BTM was applied and secured to the defect. Postoperative care involved paraffin gauze. The patient exhibited excellent aesthetic results with minimal scarring. Outcome measures, including the FACE-Q Skin Cancer Module and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), demonstrated significant improvements in appearance-related concerns, psychosocial well-being, and daily functioning. This report highlights the innovative use of NovoSorb® BTM and secondary intention healing for rhinophyma reconstruction. The successful outcome, supported by validated patient-reported outcome measures, suggests that BTM may be a valuable tool in similar cases, offering a new avenue for achieving both functional and aesthetic goals.
Keywords: aesthetic surgery; biodegradable scaffold; case report; dermatology case report dlqi (dermatology life quality index); dlqi; face-q; face-q scale; nasal reconstruction; novosorb; polynovo.
Copyright © 2025, Kyriazidis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix for Functional and Aesthetic Outcomes in Hand Soft-tissue Defect: A 3-year Retrospective Study.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Jun 25;13(6):e6909. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006909. eCollection 2025 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40567430 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable temporizing matrix utilization on a pediatric burn following an exploratory laparotomy.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2025 Feb 5;38(4):564-566. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2025.2458984. eCollection 2025. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2025. PMID: 40557188 Free PMC article.
-
Case Series of Reconstruction Applying NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporising Matrix: Preliminary Practice and Findings in the United Kingdom.Eplasty. 2025 Jun 5;25:e20. eCollection 2025. Eplasty. 2025. PMID: 40661099 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics and antiseptics for surgical wounds healing by secondary intention.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 29;3(3):CD011712. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011712.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27021482 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological, functional and neurological outcomes of craniectomy versus cranial vault remodeling for isolated nonsyndromic synostosis of the sagittal suture: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Sep;13(9):309-68. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2470. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26470674
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
