A Case of Behçet's Disease Initially Presenting With Acute Dyspnea Due to Subglottitis
- PMID: 40786345
- PMCID: PMC12335347
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87684
A Case of Behçet's Disease Initially Presenting With Acute Dyspnea Due to Subglottitis
Abstract
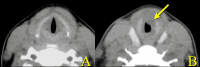
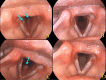
We report the case of a 17-year-old female patient who was referred to our department for acute dyspnea. She had noticed erythema all over her body and suddenly noticed severe hoarseness, cough, and wheezing three days before her presentation. Fiberscopy revealed subglottic swelling and aphthae. Subglottitis was diagnosed and intravenous corticosteroids and antibiotics were administered. Subsequently, oral ulcers, genital ulcers, and systemic papules were noted. Histologic examination of the skin suggested Behçet's disease. Behçet's disease is an inflammatory disorder that can affect multiple areas of the body, including the mucous membranes of the mouth and genital region, eyes, skin, and joints. To our knowledge, acute dyspnea due to subglottitis has never been reported in patients with Behçet's disease.
Keywords: apremilast; behçet’s disease; dyspnea; endoscopy; larynx; pseudocroup; subglottic stenosis.
Copyright © 2025, Saigo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interventions for the management of oral ulcers in Behçet's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 25;2014(9):CD011018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011018.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25254615 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of adalimumab in the treatment of intestinal Behçet's disease in children.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 30;13:1619065. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1619065. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40661890 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Rowell Syndrome: Excellent Response to Oral Cyclosporine.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):170-171. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654218
-
[Upper Gastrointestinal Involvement in Behcet's Disease].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 25;85(2):170-178. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2024.148. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40276835 Korean.
References
-
- Management of subglottic stenosis in infancy and childhood. Triglia JM, Nicollas R, Roman S. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004059900225. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000;257:382–385. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
