Ehrlichiosis Manifesting as Septic Shock and Respiratory Failure With Alveolar Hemorrhage in an Immunocompetent Patient
- PMID: 40786413
- PMCID: PMC12332641
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87581
Ehrlichiosis Manifesting as Septic Shock and Respiratory Failure With Alveolar Hemorrhage in an Immunocompetent Patient
Abstract
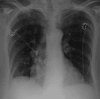
Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial infection transmitted through the bite of an infected lone star tick. The disease presents as a flu-like illness that is typically mild and self-limited. However, it can progress to severe disease with multiorgan involvement and numerous complications. We present a case of a 75-year-old immunocompetent female patient who developed septic shock and respiratory failure with alveolar hemorrhage after tick exposure. She was diagnosed with ehrlichiosis based on molecular testing via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and completed a 10-day course of doxycycline with clinical improvement. Alveolar hemorrhage is a rare but serious complication of ehrlichiosis. This case emphasizes the importance of detailed history taking and the value of pattern recognition to facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment of ehrlichiosis, which is necessary for improved patient outcomes.
Keywords: alveolar hemorrhage; doxycycline; ehrlichia chaffeensis; ehrlichiosis; lone star tick.
Copyright © 2025, Sommers et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Ventilator Management(Archived).2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28846232 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Ehrlichia chaffeensis: a prevalent, life-threatening, emerging pathogen. Walker DH, Ismail N, Olano JP, McBride JW, Yu XJ, Feng HM. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17060980/ Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2004;115:375–382. - PMC - PubMed
-
- The importance of early treatment with doxycycline in human ehrlichiosis. Hamburg BJ, Storch GA, Micek ST, Kollef MH. Medicine (Baltimore) 2008;87:53–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources