Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 40786481
- PMCID: PMC12328262
- DOI: 10.31662/jmaj.2025-0190
Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
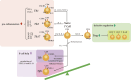
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by heterogeneous clinical manifestations and diverse autoantibody production. Despite advances in treatment, many patients experience disease flares throughout their lives, and current biomarkers like anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies and serum complement levels have limitations in accurately reflecting disease activity. This review examines emerging and established biomarkers for SLE diagnosis, disease activity monitoring, and treatment response prediction. We discuss immune cell subsets as potential biomarkers, focusing on plasmacytoid dendritic cells, T cell and B cell subsets, especially focused on T cell subsets. The review highlights how imbalances in these cellular populations correlate with disease activity and specific organ involvement. Furthermore, we discuss cytokines, chemokines, autoantibodies, and complement as biomarkers in SLE. The identification and validation of reliable biomarkers in SLE will ultimately improve clinical decision-making regarding treatment selection, glucocorticoid tapering, and prediction of disease remission, leading to more personalized and effective management strategies.
Keywords: biomarker; cytokine; immune cell subset; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © Japan Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Michihito Kono reports grants and/or speaking fees from AbbVie Inc., Asahi-Kasei Co., Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca Plc., Ayumi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Gilead Sciences K.K., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kowa Co. Ltd., Kyocera Co., Ltd., Lotte CO., LTD., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Nippon Shinyaku CO., LTD., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Mochida Pharmaceutical CO., LTD., Pfizer Inc., Sandoz., Taiju Life Social Welfare Foundation, Taisho Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Terumo Co., Ltd., UCB Japan Co. Ltd. and Yamazaki Baking CO., LTD., outside the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Lupus Check 5 Tool: A Practical Approach to Initiating Treatment Reviews in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Rheumatol Ther. 2025 Aug;12(4):731-740. doi: 10.1007/s40744-025-00770-w. Epub 2025 May 30. Rheumatol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40445564 Free PMC article.
-
'Information is power': A qualitative exploration of co-producing education resources about cardiovascular disease in partnership with women living with lupus.Womens Health (Lond). 2025 Jan-Dec;21:17455057251351736. doi: 10.1177/17455057251351736. Epub 2025 Jul 4. Womens Health (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40613440 Free PMC article.
-
Are anti-nucleosome antibodies a better diagnostic marker than anti-dsDNA antibodies for systemic lupus erythematosus? A systematic review and a study of metanalysis.Autoimmun Rev. 2012 Dec;12(2):97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Autoimmun Rev. 2012. PMID: 22810055
-
Association between Unsaturated Fatty Acid-Type Diet and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 20;16(12):1974. doi: 10.3390/nu16121974. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931327 Free PMC article.
-
B cell-targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus: Current status and perspectives.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Sep;239:117018. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.117018. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40473226 Review.
References
-
- Tsokos GC. The immunology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol. 2024;25(8):1332-43. - PubMed
-
- Hisada R, Kono M. Potential therapies targeting metabolic pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus Clin Immunol. 2024;263:110224. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita M, Sakai R, Yokogawa N, et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus and age-stratified treatment trends in the Japanese population: a cross-sectional study based on the National Database of Health Insurance Claims. Mod Rheumatol. 2025:roaf020. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, Atsumi T, Okada M, et al. Disease activity and glucocorticoid tapering patterns in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with anifrolumab: post hoc analysis of the Japanese subpopulation of the TULIP-2 study. Mod Rheumatol. 2025;35(3):470-7. - PubMed
-
- Kono M, Yasuda S, Kato M, et al. Long-term outcome in Japanese patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2014;23(11):1124-32. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
