The effect of ubiquitination and deubiquitination to imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- PMID: 40786504
- PMCID: PMC12331490
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1581920
The effect of ubiquitination and deubiquitination to imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Abstract
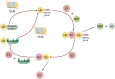
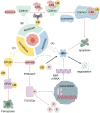
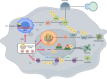
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is the most common mesenchymal tumor. Imatinib, as a receptor-type tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), becomes a first-line drug for adjuvant therapy and prognosis. However, patients are facing with the problem of primary and secondary drug resistance when using imatinib, which affects the effect of imatinib. Thus, it is particularly important to explore the mechanism of drug resistance. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination process have been proofed to performance as posttranslational modifications (PTMs) to influence the occurrence and progression of most tumors. Hence, we attach importance to these mechanisms and found that GIST resistance may be related to ubiquitination and deubiquitination in regulating exosome secretion, autophagy, apoptosis and ferroptosis. Through clarifying these connections, this review aims to offers insights and hope for therapeutic advancements of imatinib-resistant GIST patients and the use of specific ubiquitin modifications as markers in the future.
Keywords: deubiquitination modification; drug resistance; gastrointestinal stromal tumors; imatinib; ubiquitination modifications.
Copyright © 2025 Huo, Li, Yang, Wang, Zhao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

