Nivolumab plus cabozantinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: real-world evidence from the international ARON-1 study
- PMID: 40786505
- PMCID: PMC12331508
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1605282
Nivolumab plus cabozantinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: real-world evidence from the international ARON-1 study
Abstract
Introduction: Four approved immune-based combinations for untreated metastatic renal carcinoma have demonstrated survival benefits. The ARON-1 study (NCT05287464) analyzed real-world data of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving first-line immuno-oncology combinations. This sub-analysis is focused on the nivolumab plus cabozantinib effectiveness.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study across 52 centers in 17 countries, including patients with metastatic renal carcinoma treated with first-line nivolumab plus cabozantinib, regardless of histologic characteristics, performance status, or risk by IMDC prognostic model. Patients with incomplete medical data were excluded. The primary objective of this sub-analysis of the ARON-1 study was to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and safety.
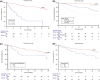
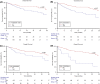
Results: A total of 333 patients were treated with nivolumab plus cabozantinib, clinical characteristics included ECOG performance status ≥2 20%, non-clear cell histology 16%, sarcomatoid de-differentiation 12%, and poor-risk by IMDC 28%. At a median follow-up of 15.9 months (95%CI 11.2-44.0), the median overall survival was not reached (40.0-NR), the probability of survival at 2 years was 75%, while median progression free survival was 33.7 months (95%CI 21.1-38.9). In the entire cohort, an objective response was observed in 58%, with 6% complete responses, and a median duration of response of 38.9 months (95%CI 33.7-NR). At multivariate analysis, adverse prognostic factors for overall survival included ECOG performance status ≥2, sarcomatoid de-differentiation, brain and bone metastases, and poor IMDC group. In the safety analysis, the incidence of grade 3 or higher toxicity was 37%, with hypertension and hand-foot syndrome being the most frequent adverse events.
Conclusion: The findings in the present real-world study reaffirm the clinical benefits and safety of the nivolumab plus cabozantinib combination across all subgroups, including populations that are generally excluded from clinical trials for whom data is often missing. Poor performance status, sarcomatoid de-differentiation, bone or central nervous system metastases and IMDC poor risk group were confirmed as negative prognostic factors.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; metastatic renal cell carcinoma; nivolumab plus cabozantinib; non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma; real-world evidence.
Copyright © 2025 Bourlon, Galli, Grande, Park, Melichar, Schieber, Juan-Fita, Ürün, Molina-Cerrillo, Alonso-Gordoa, De Giorgi, Kucharz, Pérez Calabuig, Conteduca, Taha, Rescigno, Abu-Sini, Spinelli, Manneh Kopp, Salfi, Bhuva, Valdez-Sandoval, Mendez-Bribiesca, Fiala, Buti, Marques Monteiro, Bamias, Ghosn, Massari, Ansari and Santoni.
Conflict of interest statement
MB has received honoraria from Adium, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, IPSEN, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, MSD, Pfizer, Tecnofarma. Brissto Myers Squibb and Ipsen honoraria are related to the combination therapy reported herein. LG declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. EG has received honoraria from AbbVie, Adium, Advanced Accelerator Applications, AMGEN, Angelini, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, AVEO, Bayer, Blueprint, Bristol Myers Squibb, Clovis-Oncology, Dr. Reddy’s, Eisai, Esteve, Eusa Pharma, GSK, IPSEN, ITM-Radiopharma, Janssen, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, ONCODNA Biosequence, Palex, Pfizer, Raffo, Roche, Tecnofarma, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Zodiac; has received institutional research funding from Astellas, Astra Zeneca, IPSEN, Lexicon, Merck KGaA, MTEM/Threshold/Tersera, Nanostring Technologies, Pfizer, Roche; and has received travel and accommodation expenses from Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Janssen, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech. SP declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. BM has received research funding, honoraria, and non-financial or other support from Roche, Pfizer, BMS, Astellas, Novartis, MSD, Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Eisai, and E. Lilly. TS declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. YÜ has served on advisory boards for Abdi-Íbrahim, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Deva, Eczacıbaşı, Gen ilaç, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche. And has received honoraria or has served as consultant for Abdi-Íbrahim, Astellas, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Deva, Eczacıbaşı, Gen ilaç Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche. JM-C declares consultant, advisory or speaker roles for IPSEN, Roche, Pfizer, Sanofi, Janssen, and BMS. JMC has received research grants from Pfizer, IPSEN and Roche. TA-G has received research funding, honoraria, and non-financial or other support from IPSEN, Adacap, Pfizer, Sanofi, EISAI, Lilly, Bayer, Janssen, BMS, Astellas, Novartis, Roche, and Merck. UD Reports a consulting or advisory role for Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine formerly Janssen, Merck KGaA, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Pfizer Inc. Travel, accommodation, and/or expenses from Ipsen, AstraZeneca and Pfizer. Research funding Institution from AstraZeneca, Roche, and Sanofi. JK honoraria for consultations, lectures or educational events: Angelini, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, IPSEN, Johnson&Johnson, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer. Research Funding: Novartis. All unrelated to the present paper. VC has served as a consultant/advisory board member for Johnson&Johnson, Astellas, Merck, AstraZeneca, Amgen, EISAI, Recordati, Novartis and Bayer and has received speaker honoraria or travel support from Astellas, Johnson&Johnson, Ipsen, Bayer, Astrazeneca, Gilead, GSK and BristolMyers Squibb. TT reports institutional support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer, and receiving honoraria from BMS, MSD, Merck-Serono and Pfizer. GS speakear/advisory: B,S, Janssen, Novartis, Roche, Bayer. RK Clinical research: MSD, BMS, AstraZeneca, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Abbvie, Amgen, Jannsen. Speaker/advisory: MSD, BMS, Astrazeneca, Janssen, Astellas, Tecnofarma, Pfizer, GSK, Ipsen, Janssen, Bayer, Eli Lilly, Roche, Novartis, Adium, Amgen, Merck Serono. OF received honoraria from Roche, Janssen, GSK, MSD, BMS, Pierre Fabre and Pfizer for consultations and lectures unrelated to this project. SB has received honoraria for speaking at scientific events and advisory roles from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Merck, Eisai, MSD, Novartis, Gentili, Astellas and Pfizer and research funding from Novartis and Pfizer. FMM Research support was provided by Janssen and Merck Sharp Dome. Honoraria from Janssen, Ipsen, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Merck Sharp Dome. Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Ipsen, Novartis, Merck, Merck Sharp Dome and Adium. Ownership: BIO, Brazilian Information Oncology. All are unrelated to this study. AB has received honoraria, advisory and research support from MSD, BMS, AZ, Ipsen and Astellas. FM has received research support and/or honoraria from Astellas, BMS, Janssen, Ipsen, MSD and Pfizer outside the submitted work. MS has received research support and honoraria from Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, MSD, Astellas, A.A.A. and Bayer, all unrelated to the present paper. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Tannir NM, Albigès L, McDermott DF, Burotto M, Choueiri TK, Hammers HJ, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 8-year follow-up results of efficacy and safety from the phase III CheckMate 214 trial. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:1026–38. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.07.727, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulières D, Waddell T, Stus V, Gafanov R, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:1563–73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

