Remarkable tumor response to Iruplinalkib in a 14-year-old girl with ALK-positive advanced metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a case report
- PMID: 40786512
- PMCID: PMC12331475
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1645580
Remarkable tumor response to Iruplinalkib in a 14-year-old girl with ALK-positive advanced metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a case report
Abstract
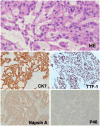
Targeted therapies for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) generally extend survival and alleviate symptoms. However, significant tumor reduction or complete remission remains rare. We report a rare case of a 14-year-old girl, whose father and grandfather both had lung cancer, diagnosed with advanced, multi-site metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC. She was treated with Iruplinalkib, a newly approved targeted therapy in China, resulting in remarkable tumor shrinkage. The patient presented with severe symptoms, including persistent cough, pain, and hemoptysis. A lung CT scan revealed a large mass, which was pathologically diagnosed as pulmonary adenocarcinoma. After initiating Iruplinalkib therapy, the primary tumor rapidly decreased in size by 80.3%, from 132 mm × 97 mm to 26 mm × 21 mm, within one month. Most metastatic lesions also showed significant regression. By six months, the pulmonary tumor had almost disappeared. This case underscores the potential of Iruplinalkib, which is currently not available outside of China, to induce rapid and profound tumor regression in ALK-positive NSCLC, particularly in adolescent patients with aggressive clinical presentations. We hope that the anticancer efficacy of Iruplinalkib will be recognized globally and that it will become accessible to ALK-positive lung cancer patients worldwide.
Keywords: ALK fusion gene mutation; Iruplinalkib; case report; non-small cell lung cancer; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Du, Sun, Tao, Zhang, Li, Liu, Wei, Tian and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Xia Y, Tian P, Zhou M, Zhao J, Jin Y, Guo Z, et al. Ensartinib for advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with MET exon 14 skipping mutations (EMBRACE): a multi-center, single-arm, phase 2 trial. J eClinicalMedicine. (2025) 81:103099. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103099, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

