A Novel, Non-Invasive AI-Based Telemonitoring System for Heart Failure: Detection of Undiagnosed Hyperthyroidism in an Asymptomatic Patient
- PMID: 40786544
- PMCID: PMC12331272
- DOI: 10.12890/2025_005420
A Novel, Non-Invasive AI-Based Telemonitoring System for Heart Failure: Detection of Undiagnosed Hyperthyroidism in an Asymptomatic Patient
Abstract
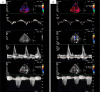
Background: Untreated thyroid disorders may precipitate heart failure (HF) decompensation. Assessment of cardiac filling pressures may aid in the early detection and prevention of clinical decompensation. Therapy guided by monitoring of cardiac filling pressures has been shown to improve quality of life and survival and reduce hospitalizations of individuals with HF. We have developed a non-invasive method to assess left ventricular filling pressures (LVFP) by analysing the photoplethysmography signal with Seeling HeartCore technology (Seerlinq, Bratislava, Slovakia).
Case description: A 99-year-old female visited the clinic for a routine cardiac check-up. Laboratory investigations showed elevated NTproBNP and moderately elevated high sensitive troponin T. HeartCore algorithm indicated elevated LVFP. As part of the evaluation of worsening of sub-clinical HF, extended laboratory tests revealed low thyroid-stimulating hormone with high free thyroxine levels indicating increased thyroid function. The endocrinologist diagnosed hyperthyroidism with multinodular goitre and prescribed thiamazole. To prevent progression to clinical HF decompensation, the dose of furosemide was increased. At 4 months, during scheduled cardiac follow-up, the patient was clinically doing well, without any signs or symptoms of HF.
Discussion: Remote monitoring devices that track pressures in the pulmonary artery require invasive implantation and are associated to potential complications. The high cost of these devices presents a significant barrier to widespread use. SEERLINQ is a novel system for remote haemodynamic monitoring based on non-invasive assessment of LVFP, presenting a promising alternative to current invasive methods.
Conclusion: This case underscores the potential benefits of this technology in the early recognition of pre-clinical deterioration and its implementation for remote home monitoring in patients with HF.
Learning points: Untreated thyroid disorders in patients with heart failure (HF) can exacerbate signs and symptoms of HF.Left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP) rises 3-4 weeks before HF symptoms. Echocardiographic assessment of LVFP can be challenging in patients with atrial fibrillation or paced rhythms.Photoplethysmography-based analysis could be utilized to assess LVFP, enabling remote monitoring of HF patients and potentially preventing HF decompensation and hospitalization.
Keywords: Heart failure; artificial intelligence; hyperthyroidism; photoplethysmography; telemonitoring.
© EFIM 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: All authors are shareholders and/or employees of Seerlinq Ltd. AB, BB and NJ are founders of Seerlinq Ltd. AB also founded Premedix Academy.
Figures

References
-
- Zile MR, Bennett TD, St John Sutton M, Cho YK, Adamson PB, Aaron MF, et al. Transition from chronic compensated to acute decompensated heart failure: pathophysiological insights obtained from continuous monitoring of intracardiac pressures. Circulation. 2008;118:1433–1441. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.783910. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caiani EG, Kemps H, Hoogendoorn P, Asteggiano R, Böhm A, Borregaard B, et al. Standardized assessment of evidence supporting the adoption of mobile health solutions: A Clinical Consensus Statement of the ESC Regulatory Affairs Committee: Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), the Association of Cardiovascular Nursing & Allied Professions (ACNAP) of the ESC, the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC, the ESC Young Community, the ESC Working Group on e-Cardiology, the ESC Council for Cardiology Practice, the ESC Council of Cardio-Oncology, the ESC Council on Hypertension, the ESC Patient Forum, the ESC Digital Health Committee, and the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2024;5:509–523. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztae042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ong MK, Romano PS, Edgington S, Aronow HU, Auerbach AD, Black JT, et al. Effectiveness of Remote Patient Monitoring After Discharge of Hospitalized Patients With Heart Failure: The Better Effectiveness After Transition -- Heart Failure (BEAT-HF) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:310–318. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
