Immunomodulatory biomaterials for osteoarthritis: Targeting inflammation and enhancing cartilage regeneration
- PMID: 40786659
- PMCID: PMC12332962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102100
Immunomodulatory biomaterials for osteoarthritis: Targeting inflammation and enhancing cartilage regeneration
Abstract
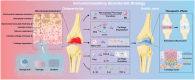
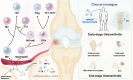
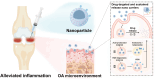
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent joint disorder characterized by progressive cartilage degradation, impaired mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) function, and chronic inflammation, ultimately leading to irreversible structural damage and functional impairment. Despite its high global burden, no regulatory agency has yet approved a disease-modifying therapy for OA, and effective interventions to halt or delay its progression remain a major challenge. Recent research highlights the pivotal role of the immune system in OA pathogenesis, with immunomodulatory biomaterials emerging as a promising strategy to simultaneously regulate inflammatory responses and promote tissue regeneration. These biomaterials, by leveraging their biocompatibility and immunoregulatory properties, offer a transformative alternative to conventional OA therapies, which predominantly focus on symptom management rather than targeting the underlying disease mechanisms. In this review, we comprehensively examine various immunomodulatory biomaterial strategies designed to mitigate OA progression. We first elucidate the immune landscape of OA, detailing the interplay between inflammation and disease pathophysiology. Next, we explore the latest advancements in immunomodulatory biomaterials, including nanoparticles (NPs), hydrogels, and scaffolds, highlighting their potential to reshape OA treatment. Finally, we discuss existing challenges and propose future directions for optimizing biomaterial-based immunotherapies to enhance OA management.
Keywords: Cartilage regeneration; Drug delivery; Immune response; Immunomodulatory biomaterials; Osteoarthritis; Responsive biomaterials.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Ma Y., Yang H., Zong X., Wu J., Ji X., Liu W., Yuan P., Chen X., Yang C., Li X., Chen Y., Xue W., Dai J. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274 - PubMed
-
- Mobasheri A., Rayman M.P., Gualillo O., Sellam J., van der Kraan P., Fearon U. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017;13(5):302–311. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

