How to Deal with Bladder Stones Associated with Exposed Intravesical Mesh
- PMID: 40786677
- PMCID: PMC12334095
- DOI: 10.4103/gmit.gmit_86_24
How to Deal with Bladder Stones Associated with Exposed Intravesical Mesh
Abstract
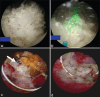
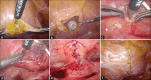
We present the management of seven patients who were diagnosed with bladder stone associated with exposed intravesical mesh after transvaginal mesh (TVM) surgery for pelvic organ prolapse. The TVM may be exposed inside the bladder which can result in urinary stone formation. Several treatment modalities have been proposed such as laser lithotripsy, transurethral resection, and open or laparoscopic resection of exposed mesh. However, the optimal route of treatment remains inconclusive. In our series, two cases were managed by transurethral resection and one of them had recurrence. Five cases were managed by laparoscopic resection and one of them had recurrence. Two recurrent cases underwent laparoscopic resection and then no recurrence occurred. No intraoperative or postoperative complications occurred. Although there is limited evidence, we recommend laparoscopic resection for the treatment of intravesical mesh exposure. Offering transurethral resection as an initial management of intravesical mesh exposure is possible with careful discussion about the recurrence rate.
Keywords: Bladder stone; intravesical mesh exposure; management; transvaginal mesh; treatment.
Copyright: © 2025 Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Olsen AL, Smith VJ, Bergstrom JO, Colling JC, Clark AL. Epidemiology of surgically managed pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;89:501–6. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez Garzon HJ, Jacquemet B, Mottet N, Kleinclauss F, Riethmuller D, Ramanah R. Endoscopic lithotripsy and vaginal excision of a calcified bladder-mesh extrusion. Int Urogynecol J. 2016;27:1113–5. - PubMed
-
- Araco F, Gravante G, Piccione E. Bladder erosion after 2 years from cystocele repair with type I polypropylene mesh. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009;20:731–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
