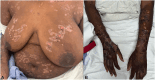
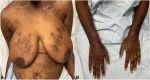
Recalcitrant epidermolysis bullosa acquisita treated with upadacitinib as a bridge to rituximab
- PMID: 40787064
- PMCID: PMC12328672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2025.06.022
Recalcitrant epidermolysis bullosa acquisita treated with upadacitinib as a bridge to rituximab
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; autoimmune blistering disease; bridging therapy; epidermolysis bullosa acquisita; mechanobullous EBA; refractory dermatologic disease; rituximab; upadacitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
None disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Case Report of the Use of Rituximab and the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity Scoring Index (EBDASI) in a Patient with Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita with Extensive Esophageal Involvement.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Dec;26(4):325-328. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 30665483
-
A case of recalcitrant epidermolysis bullosa acquisita responsive to rituximab therapy.Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):241-4. doi: 10.1111/pde.12006. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 23106762
-
Clinical response of severe mechanobullous epidermolysis bullosa acquisita to combined treatment with immunoadsorption and rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies).Arch Dermatol. 2007 Feb;143(2):192-8. doi: 10.1001/archderm.143.2.192. Arch Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17309999
-
The use of rituximab in treatment of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: Three new cases and a review of the literature.Dermatol Ther. 2018 Nov;31(6):e12726. doi: 10.1111/dth.12726. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Dermatol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30284354 Review.
-
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013 Oct;27(10):1204-13. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12096. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013. PMID: 23368767 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
