Molecular Mechanisms of Chronic Pain and Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 40787071
- PMCID: PMC12331885
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70325
Molecular Mechanisms of Chronic Pain and Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
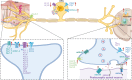
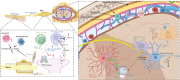
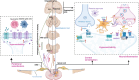
Chronic pain imposes incalculable health and economic burdens, affecting more than 30% of the global population in published studies. Optimal management of chronic pain is imperative for individuals experiencing such distress. Nevertheless, the current approaches to chronic pain assessment and treatment fail to meet clinical requirements. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for precision medicine approaches to effectively manage chronic pain. Chronic pain can be classified into three categories: nociceptive (resulting from tissue injury), neuropathic (caused by nerve injury), or nociplastic (arising from a sensitized nervous system). These classifications significantly impact the evaluation and treatment decisions at all levels. Significantly, in practice, there is substantial overlap in chronic pain mechanisms among patients and within different types of chronic pain. The application of precision medicine is imperative in the management of chronic pain. This review offers a comprehensive overview of the distinctive molecular mechanisms underlying nociceptive, neuropathic, and nociplastic pain, including immune responses, ion channels, monoaminergic imbalance, and neuroinflammation. Subsequently, we summarized the status quo of nociceptive, neuropathic, and nociplastic pain manipulation. Last, we explored the advances in pain management strategies for chronic pain that are making significant progress toward their clinical implementation.
Keywords: molecular mechanism; neuropathic pain; nociceptive pain; nociplastic pain; therapeutic interventions.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ketamine in Acute and Chronic Pain Management.2023 Sep 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Sep 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30969646 Free Books & Documents.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Oxycodone for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 23;(6):CD010692. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010692.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 28;7:CD010692. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010692.pub3. PMID: 24956205 Updated.
References
-
- Treede R. D., Rief W., Barke A., et al., “Chronic Pain as a Symptom or a Disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD‐11),” Pain 160, no. 1 (2019): 19‐27. - PubMed
-
- Sommer C. and Rittner H., “Pain Research in 2023: Towards Understanding Chronic Pain,” Lancet Neurology 23, no. 1 (2024): 27‐28. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
