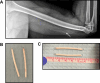
Removal of 2-Rod Subdermal Implant Identified on X-Ray: A Case Report
- PMID: 40787161
- PMCID: PMC12331526
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.70737
Removal of 2-Rod Subdermal Implant Identified on X-Ray: A Case Report
Abstract
Case report of a 37-year-old Colombian patient seeking removal of a subdermal implant, initially believed to be the single-rod Nexplanon implant. However, following extraction, it was identified as the 2-rod international subdermal implant alternative, Jadelle. This case highlights the need for US health care providers to be cognizant of non-US subdermal alternatives given the rising presence of foreign-born patients they may encounter in their practice.
Keywords: Jadelle; Nexplanon; long‐acting reversible contraception; subdermal implant.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bahamondes L., Fernandes A., Monteiro I., and Bahamondes M. V., “Long‐Acting Reversible Contraceptive (LARCs) Methods,” Best Practice & Research. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology 66 (2020): 28–40. - PubMed
-
- Grimes D. A., “Forgettable Contraception,” Contraception 80, no. 6 (2009): 497–499. - PubMed
-
- Teal S. and Edelman A., “Contraception Selection, Effectiveness, and Adverse Effects: A Review,” Journal of the American Medical Association 326, no. 24 (2021): 2507–2518. - PubMed
-
- Rowlands S. and Searle S., “Contraceptive Implants: Current Perspectives,” Open Access Journal of Contraception 5 (2014): 73–84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources