Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Mass in Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- PMID: 40787170
- PMCID: PMC12334272
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.70784
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Mass in Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Abstract
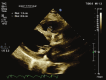
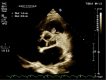
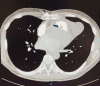
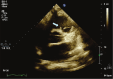
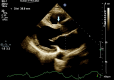
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is well known for its association with arterial and venous thrombosis. Intracardiac thrombosis-more often involving the right atrium-is a serious manifestation of the disease. We describe an APS case with a thrombosis in the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), which underwent regression after aggressive anticoagulation.
Keywords: antiphospholipid syndrome; intra cardiac thrombosis; right ventricular outflow tract thrombosis; transthoracic echocardiography.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Miyakis S., Lockshin M. D., Atsumi T., et al., “International Consensus Statement on an Update of the Classification Criteria for Definite Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS),” Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 4, no. 2 (2006): 295–306. - PubMed
-
- Barbhaiya M., Zuily S., Naden R., et al., “The 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria,” Arthritis and Rheumatology 75, no. 10 (2023): 1687–1702. - PubMed
-
- Soltész P., Szekanecz Z., Kiss E., and Shoenfeld Y., “Cardiac Manifestations in Antiphospholipid Syndrome,” Autoimmunity Reviews 6, no. 6 (2007): 379–386. - PubMed
-
- Turiel M., Muzzupappa S., Gottardi B., Crema C., Sarzi‐Puttini P., and Rossi E., “Evaluation of Cardiac Abnormalities and Embolic Sources in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome by Transesophageal Echocardiography,” Lupus 9, no. 6 (2000): 406–412. - PubMed
-
- Erdogan D., Goren M. T., Diz‐Kucukkaya R., and Inanc M., “Assessment of Cardiac Structure and Left Atrial Appendage Functions in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Transesophageal Echocardiographic Study,” Stroke 36, no. 3 (2005): 592–596. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

