Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Green Synthesized Poly(MBAAm- co-VSPI) Zwitterionic Nanoparticles for the Removal of Reactive Dyes
- PMID: 40787350
- PMCID: PMC12332782
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00096
Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Green Synthesized Poly(MBAAm- co-VSPI) Zwitterionic Nanoparticles for the Removal of Reactive Dyes
Abstract
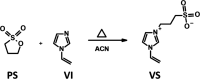
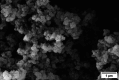
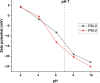
Reactive dyes are well known for their color fastness. However, they also display a tendency toward carcinogenicity and mutagenicity. Hence, among the many methods for their removal from dye wastewater, membrane technology appears to be the most viable. In this work, zwitterionic polymeric nanoparticles poly-(MBAAm-co-VSPI) were synthesized via precipitation polymerization following a free radical mechanism using N,N'-methylene bis-(acrylamide) (MBAAm) as a cross-linker and laboratory-synthesized 1-vinyl-3-(3-sulfanatopropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-ium (VSPI) as the monomer. The reaction was carried out in water by utilizing a water-soluble free radical initiator 2,2'-azobis-2-methylpropionamide dichloride (V-50). The resulting nanoparticles were analyzed using FTIR, SEM, EDS, XRD, TGA, zeta potential, DLS, and BET studies. Mixed matrix membranes were fabricated by the incorporation of laboratory-synthesized nanoparticles in the polysulfone (PSf) polymer matrix. Among the series of membranes fabricated, PM-2 showed the highest rejection of the reactive dyes, Reactive Black 5 (RB5 98%) and Reactive Orange 16 (RO16 86%), at 20 ppm concentration along with good pure water permeability of 82.34 L m-2 h-1 bar-1. Hence, this membrane has potential for the treatment of textile wastewater.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures









References
-
- Karypidis, M. ; Tarnanidis, T. ; Papachristou, E. . Treating textile effluents for sustainable fashion and green marketing. Driving Green Marketing in Fashion and Retail; IGI Global; 2024; pp 166–179. 10.4018/979-8-3693-3049-4.ch010. - DOI
-
- De Gisi S., Lofrano G., Grassi M., Notarnicola M.. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustainable Materials and Technologies. 2016;9:10–40. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2016.06.002. - DOI
-
- Al Farraj D. A., Elshikh M. S., Al Khulaifi M. M., Hadibarata T., Yuniarto A., Syafiuddin A.. Biotransformation and Detoxification of Antraquione Dye Green 3 using halophilic Hortaea sp. Int. Biodeterior Biodegradation. 2019;140:72–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.03.011. - DOI
-
- Asgher M.. Biosorption of reactive dyes: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012;223(5):2417–2435. doi: 10.1007/s11270-011-1034-z. - DOI
-
- Wu J., Wang X., Hu J., Li C., Shi L., Xia S., Cai Y., Jia R., Chen Z., Li L.. Ultra-small cesium silver bismuth bromide quantum dots fabricated by modified hot-injection method for highly efficient degradation of contaminants in organic solvent. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2025;152:577–583. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.06.011. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
