Efficacy and safety of low dose rituximab in pemphigus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40787442
- PMCID: PMC12331757
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605243
Efficacy and safety of low dose rituximab in pemphigus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab (RTX) in the treatment of pemphigus.
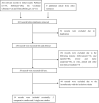
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov to identify eligible studies. Primary efficacy outcomes included complete remission (CR), relapse rates, time to disease control (TDC), time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose. Safety outcomes were assessed by meticulously documenting adverse events (AEs) and concomitant medications reported in each study.
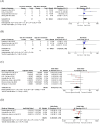
Results: The final analysis incorporated five comparative studies and nine single-arm studies investigating the efficacy and safety outcomes of low-dose RTX. Comparative data revealed no statistically significant differences between the high-dose and low-dose RTX groups in CR, relapse rates, TDC, time to CR, and cumulative corticosteroid dose. In single-arm studies, pooled CR and relapse rates were 63.2% and 28.6%, respectively. No fatal events were reported; however, severe AEs, including pneumonia and sepsis, were documented in the low-dose RTX cohort.
Conclusion: Low-dose RTX exhibited comparable clinical efficacy to high-dose RTX regimens in pemphigus management. However, clinicians should remain vigilant for potential AEs associated with low-dose RTX infusion.
Keywords: meta-analysis; pemphigus; rituximab; safety; treatment outcome.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Wang and Zuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

