Sarcopenia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: mechanisms, diagnosis, and management strategies
- PMID: 40787546
- PMCID: PMC12333762
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003584
Sarcopenia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: mechanisms, diagnosis, and management strategies
Abstract
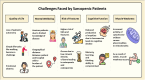
Sarcopenia affects 20%-40% of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients, significantly reducing muscle strength and functional capacity, leading to a decline in quality of life. This study reviews the impact of sarcopenia in COPD and evaluates effective therapeutic strategies. Findings suggest that pulmonary rehabilitation, combined with aerobic and resistance exercises, and supplemented with protein and vitamin D, enhances muscle function and reduces the prevalence of sarcopenia. Additionally, emerging interventions such as inspiratory muscle training, myostatin inhibitors, selective androgen receptor modulators, and hormonal therapies show promise in improving patient outcomes. A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating personalized exercise programs, targeted nutrition, and psychological support, is crucial for addressing the complex challenges of sarcopenia in COPD. Given its substantial burden, this research highlights critical strategies for optimizing care and improving functional outcomes in this high-risk population.
Keywords: COPD; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; frailty; muscle loss; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article. None.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal AK, Raja A, Brown BD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441988/ - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
