Significance of APOB/APOA1 Ratio in the Prediction of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
- PMID: 40787622
- PMCID: PMC12335912
- DOI: 10.1155/cdr/5528174
Significance of APOB/APOA1 Ratio in the Prediction of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
Abstract
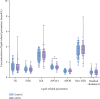
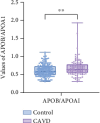
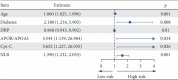
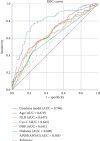
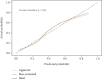
Background: Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a prevalent heart valve disease. The ratio of two apolipoproteins with distinct functions, Apolipoprotein B/Apolipoprotein A1 (APOB/APOA1), has been proposed as a novel assessment index for the evaluation of cardiovascular diseases. The aim of this article is to discuss the role of lipid parameters such as APOB/APOA1 in CAVD and the risk factors for CAVD, to develop a predictive model for CAVD, and to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of this model. Method: Patients who initially presented to the Department of Cardiology of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University between 1 January 2023 and 31 December 2023 were retrospectively identified and included in the study. Patients were divided into an aortic valve calcification group (111 cases) and a control group (201 cases) based on computed tomography (CT) findings. The clinical data, laboratory examination results, and chest CT images of the patients were collected and analyzed. A variety of statistical methods were used to analyze risk factors for CAVD, to construct a CAVD prediction model, and to assess its sensitivity and specificity. Results: Lipid parameters APOA1, APOB/APOA1, cumulative low-density lipoprotein (LDL) exposure, and non-high-density lipoprotein/high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL/HDL) were significantly associated with aortic valve calcification. Age, history of diabetes, diastolic blood pressure (DBP), APOB/APOA1, Cystatin C (Cys-c), and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are identified as independent risk factors for CAVD, and the combined model achieved an AUC of 0.796 for CAVD prediction, corresponding to a sensitivity of 0.769 and a specificity of 0.755. Conclusion: The lipid parameters APOA1, APOB/APOA1, cumulative LDL exposure, and non-HDL/HDL have been demonstrated to be associated with aortic valve calcification. Furthermore, APOB/APOA1 can be used for the prediction of CAVD, and the combination of APOB/APOA1 with age, history of diabetes, DBP, Cys-c, and NLR has better prediction performance for CAVD.
Keywords: APOB/APOA1; calcific aortic valve disease; prediction model.
Copyright © 2025 Yuxing Wang et al. Cardiovascular Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

